Figure 7. Targeted retinal overexpression of vxn promotes early retinal cell differentiation.
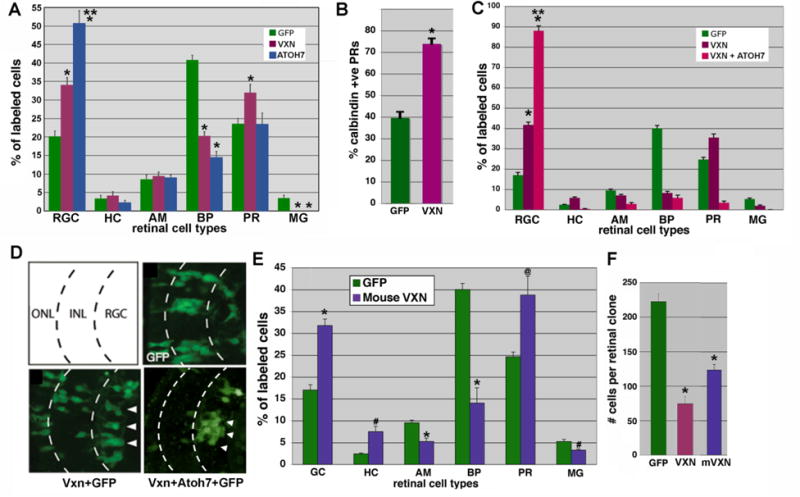
(A,B) GFP (300pg) was lipofected alone or together with Xenopus vxn (250 pg) or Xenopus atoh7 into the optic vesicle of stage 18 embryos. Embryos were cryosectioned at stage 41, and GFP-labeled retinal cell types were counted. Atoh7 expression caused a significant increase in RGCs. Vxn expression caused a significant increase in RGCs and photoreceptors, that were confirmed to be calbindin-positive cones, which are born early (B). Later born bipolar cells and Mueller glia were significantly reduced. *p<0.001 relative to GFP,** p<0.001 relative to vxn + GFP.
(C) Injection of vxn mRNA into 1 cell of a 32- cell embryo produced a 2.5-fold increase in the number of GFP-labeled RGCs as compared to injection of GFP mRNA control alone, while vxn + atoh7 caused almost 90% of labeled cells to differentiate as RGCs. *p<0.001 relative to GFP alone, ** p<0.001 relative to vxn + GFP.
(D) Schematic of 3 retinal layers: the outer nuclear layer (ONL), the inner nuclear layer (ONL), and the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer. Injection of GFP mRNA alone reproducibly labeled neuronal subtypes within all 3 layers. Vxn + GFP mRNA injection resulted in an increased number of GFP-positive cells in the RGC layer (arrowheads). Vxn + atoh7 + GFP mRNA caused almost all labeled cells to differentiate as RGCs.
(E) Injection of mRNA for mouse vxn had a similar effect, causing a significant increase in early born cell types (GCs, HCs and PRs) at the expense of later born cell types (BPs, AMs). * p<0.001, # p<0.01, @p<0.02.
(F) Injection of mRNA for either Xenopus or mouse vxn together with GFP mRNA into blastomere V1.2.1 at the 32-cell stage resulted in reduced labeled retinal clone size in stage 41 retina, consistent with reduced retinal progenitor proliferation. *p < 0.01, as compared to GFP alone.
RGC, retinal ganglion cells; HC, horizontal cells; AC, amacrine cells; BP, bipolar cells; PR, photoreceptor cells; MG, Muller glial cells.
