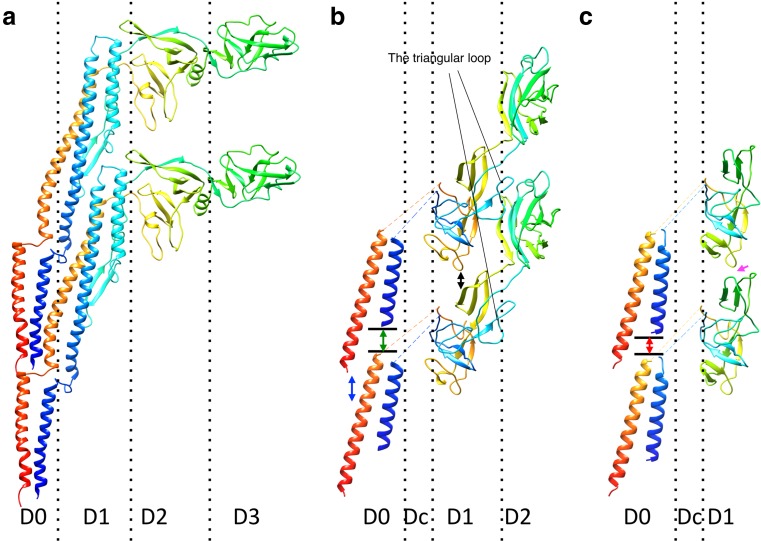
Fig. 4.
Comparison of the protofilament structures of the filament (a), the hook (b), and the rod (c). Two protein subunits in a protofilament are shown in each panel. The chains are colored in the rainbow sequence of colors from blue to red for the N- to C-terminus. The D0 and D1 helices of FliC are arranged nearly parallel to the filament axis and densely packed along the protofilament. The D0 helices of flagellar hook protein FlgE are tilted to form a gap between the axially neighboring subunits (blue two-direction arrow). The N-terminal helix of flagellar rod protein FlgG is one turn longer than that of FlgE; therefore the gap between the N-terminal helix and the axially neighboring subunit (red two-direction arrow) is shorter than that in the hook (green two-direction arrow). The D1 domains of FlgG are arranged upright to make an interaction with the neighboring subunit (magenta arrow), while those of FlgE in the hook are tilted, producing an axial gap along the protofilament (black two-direction arrow)