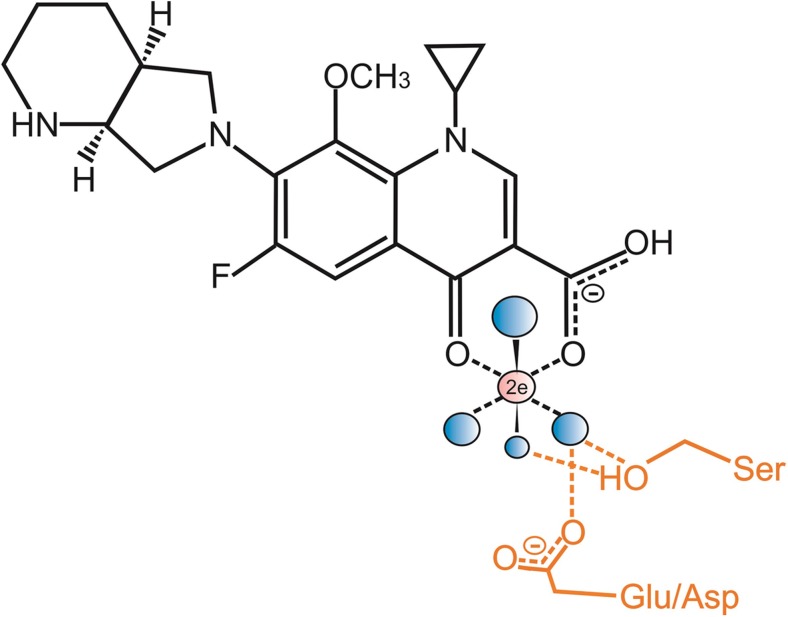
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of moxifloxacin binding to topoisomerase IV via a water-metal ion bridge, adapted and redrawn from Aldred et al. (2014) for ciprofloxacin. For clarity, the DNA has been omitted. Moxifloxacin is shown in black; the Mg2+ ion that is chelated by the C3-C4 ketoacid of the antibiotic is shown in pink; the four water molecules coordinated by the Mg2+ ion are shown in blue. The side chains of the conserved acidic Glu88 (Asp in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae) and Ser84 residues of Acinetobacter baumanii topoisomerase IV are shown in orange, together with their hydrogen bonding to the water molecules