Figure 9.
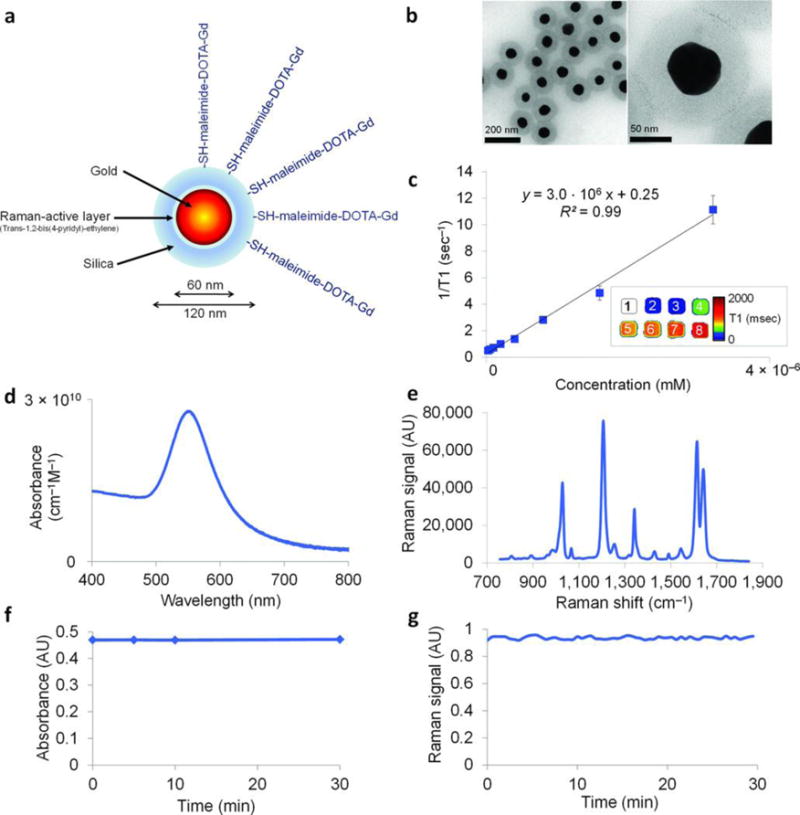
Characterization of the NPs. (A) Simplified diagram: A 60 nm gold core is surrounded by a thin Raman active layer that is protected by a 30 nm silica coating. The silica coating was further functionalized with maleimide-DOTA-Gd, which was conjugated to the thiol group on the silica. DOTA, tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid, is a chelator. (B) Transmission electron microscopy images of NPs. (C) Particle relaxivity derived from T1 maps of probe dilutions in MRI phantoms. Data represent mean of two separate phantoms containing separate probe conjugations. Inset: T1 map of a MRI phantom containing NPs at concentrations ranging from 3.2 nM (1) to 25 pM (8). (D) Optical absorbance of NPs. (E) Raman spectrum of NPs with characteristic peaks at 1,021 cm−1, 1,204 cm−1, 1,340 cm−1, 1,614 cm−1, and 1,638 cm−1. (F, G) During 30 min of continuous laser irradiation, the optical absorbance (F) and the Raman signal (G) remained constant. Adapted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: [Nature Medicine]185, copyright (2012).
