Figure 4. ERK2 regulates FOXC2‐dependent DLL4 expression in LPS‐treated HPMECs.
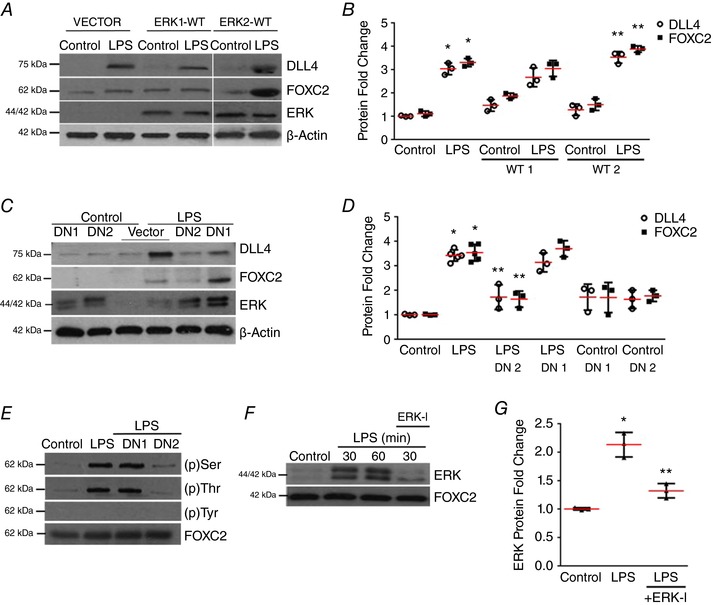
A and B, DLL4, FOXC2 and ERK protein were assessed by immunoblotting 24 h after LPS treatment in vector, wild‐type ERK1 or ERK2 plasmid (ERK1‐WT, ERK2‐WT) transfected HPMECs, and quantified by densitometry (B), P < 0.01 (*Control vs. LPS, **LPS vs. ERK2‐WT + LPS), n ≥ 3. C, DLL4, FOXC2, and ERK protein were assessed by immunoblotting 24 h after LPS treatment in vector, ERK1‐DN (DN1) or ERK2‐DN (DN2) plasmid transfected HPMECs, and quantified by densitometry (D), P < 0.001 (*Control vs. LPS; **LPS vs. ERK2‐DN + LPS), n = 3. E, FOXC2 was immunoprecipitated 30 min after LPS treatment in cells transfected with control, ERK1‐DN, ERK2‐DN plasmid with serine, threonine and tyrosine FOXC2 phosphorylation quantified, n = 3. F and G, ERK binding to FOXC2 was examined in FOXC2 immunoprecipitates obtained at 30 and 60 min after ERK‐I and LPS treatment, and quantified by densitometry (G), P < 0.01 (*Control vs. LPS; ** LPS vs. ERK‐I + LPS), n = 3. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
