Figure 6. ERK regulates FOXC2 activation and DLL4 expression in the developing lung.
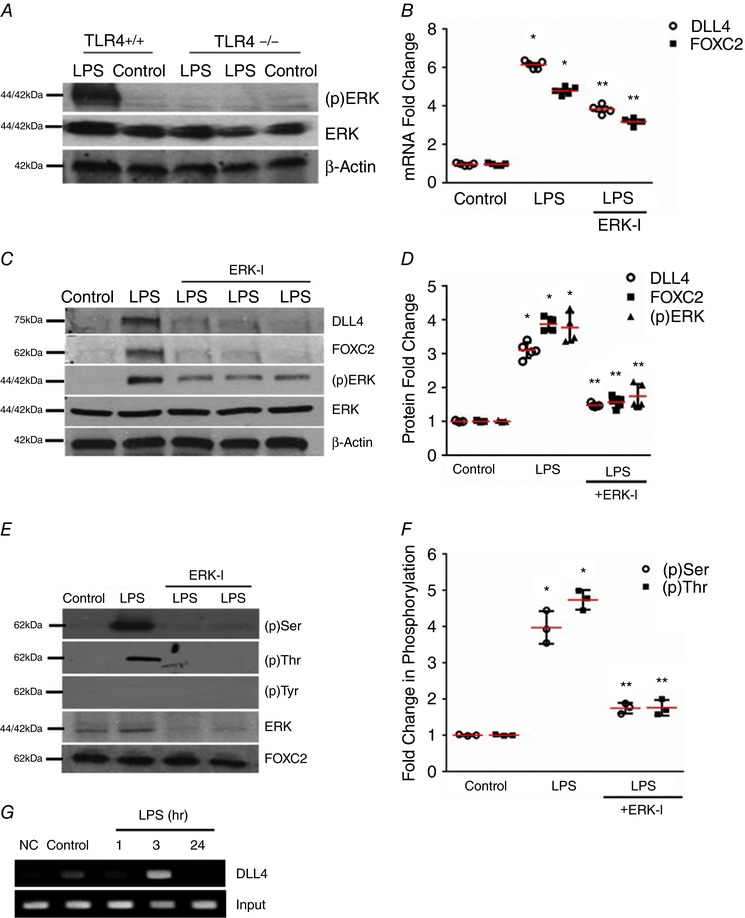
A, ERK phosphorylation was quantified by immunoblotting using an anti‐phospho ERK antibody in lung homogenates obtained from TLR4+/+ and TLR4−/− mice 24 h after i.p. LPS, n ≥ 4 mice in each group. B, lung DLL4 and FOXC2 mRNA were quantified by qRT‐PCR 24 h after i.p. LPS with or without i.p. ERK‐I (20 mg kg−1), P < 0.01 (*Control vs. LPS; **LPS vs. ERK‐I + LPS), n ≥ 3 mice in each group. C and D, DLL4, FOXC2, and (p)ERK were quantified by Western blotting 24 h after i.p. LPS with or without i.p. ERK‐I, with densitometry analysis shown graphically (D), P < 0.05 (*Control vs. LPS; **LPS vs. ERK‐I + LPS), n ≥ 4 mice. E and F, lung FOXC2 phosphorylation was examined by immunoprecipitation 3 h after i.p. LPS with or without ERK‐I, and quantified by densitometry (F), P < 0.001 (*Control vs. LPS: **LPS vs. ERK‐I + LPS), n ≥ 3. G, whole lung nuclear homogenates obtained at 1, 3, and 24 h after i.p. LPS were used for the ChIP assays to quantify binding of FOXC2 to the DLL4 promotor, n ≥ 3. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
