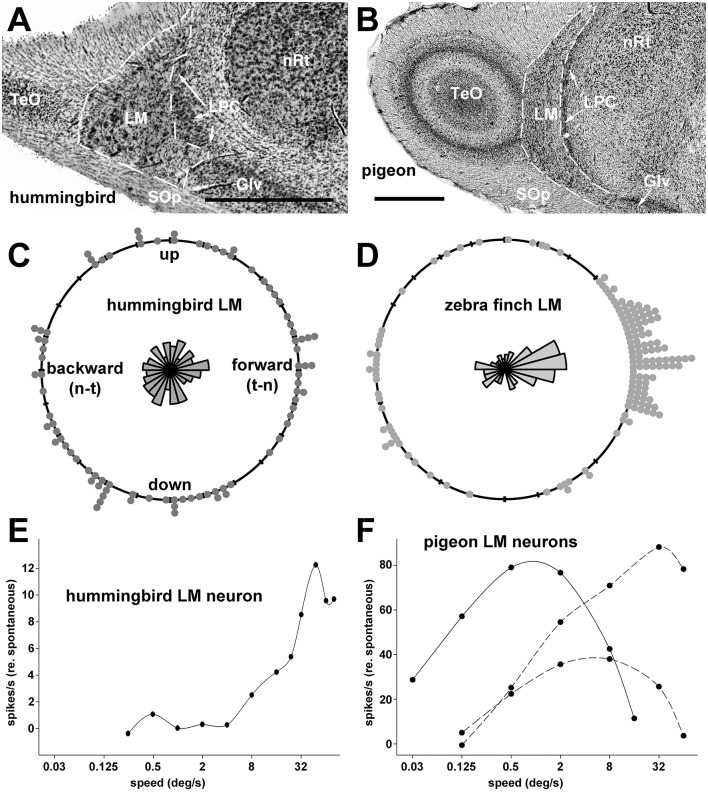
Figure 2.
Coronal sections through the pretectal nucleus lentiformis mesencephali (LM) in a hummingbird (Doryfera ludoviciae) (A, from Iwaniuk and Wylie, 2007, with permission) and a pigeon (Columba livia) (B). (C,D) Respectively show the direction preferences of LM neurons in Anna's hummingbird (Calypte anna) and zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata) (from Gaede et al., 2017, with permission). (E) Shows the speed tuning curve for a LM neuron in a Anna's hummingbird (from the data set of Gaede et al., 2017). The visual stimuli were largefield random dot patterns moving in the preferred direction. (F) Shows the speed tuning for 3 LM neurons in pigeon: (from the data set of Crowder et al., 2003). One is a “slow” neuron that preferred forward (nasal to temporal) motion (solid line), whereas the other two are “fast” neurons that preferred backward (lower dashed line) and downward (upper dashed line) motion. The visual stimulus were largefield sine wave gratings of an effective spatial frequency (1 cycle per degree [cpd] for the slow neuron, 0.25cpd for the fast neurons) drifting in the preferred directions. Other abbreviations: Glv, ventral lateral geniculate nucleus; LPC, nucleus laminaris precommissuralis; nRt, nucleus rotundas; TeO, optic tectum; SOp, stratum opticum; t-n, temporal to nasal; n-t, nasal to temporal. Scale bars; 0.5 mm in (A) 1 mm in (B).