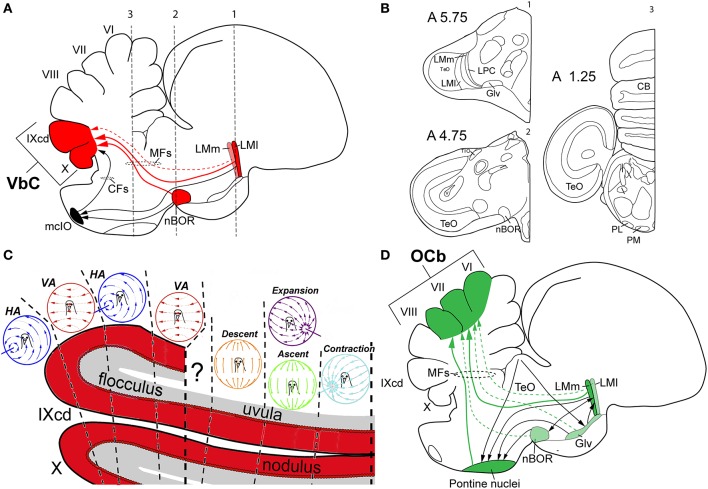
Figure 4.
Visual cerebellar pathways in birds. (A) Shows in red the optic flow pathways from the nucleus of the basal optic root (nBOR) and pretectal nucleus lentiformis mesencephalic (LM) to the vestibulocerebellum (VbC; folia IXcd and X), black arrows show projections to the medial column of the inferior olive (mcIO). (B) Shows schematic drawings of coronal sections at three different anteroposterior levels (1–3 in A) of the pigeon's brain to show the relative position of the different nuclei involve in visual pathways to the cerebellum in birds. Coordinates in the pigeon brain atlas of Karten and Hodos (1967) are shown. Adapted from Karten and Hodos (1967). (C) Shows the sagittal optic flow “zones” in the VbC. (D) Shows in green and black the extensive pretecto-ponto-cerebellar connectivity to the oculomotor cerebellum (OCb, folia VI–VII). The larger arrows with solid lines represent heavier projections, whereas the smaller arrows with dotted lines represent weaker projections. See text for details. Other abbreviations: CFs, climbing fibers; Glv, ventral lateral geniculate nucleus; HA, horizontal axis (neurons); LMl, lateral LMm, medial LM; MFs, mossy fibers; PL, lateral pontine nucleus; PM, medial pontine nucleus; VA, vertical axis (neurons).