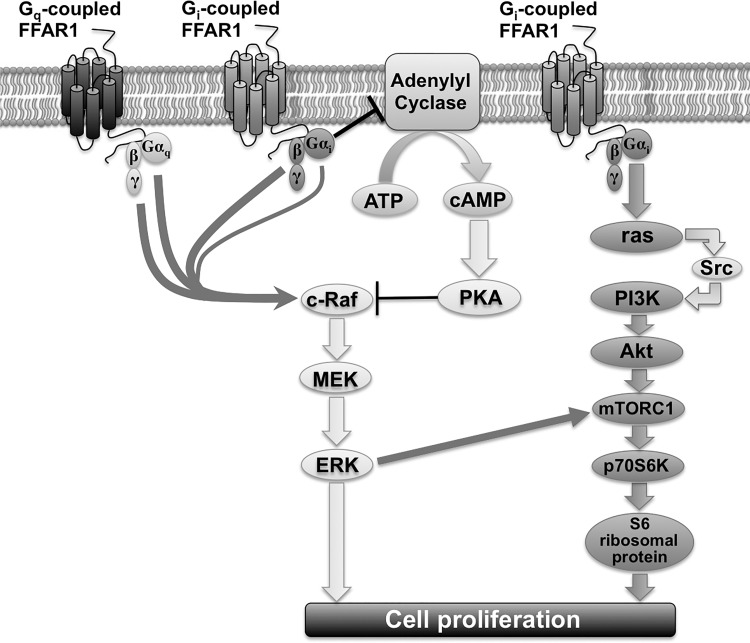
Fig. 11.
Schematic drawing of FFAR1-stimulated signaling cascade of ERK and Akt in HASM cells. Gi-coupled FFAR1 inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity, which inhibits cAMP production. Reduced cAMP production leads to decreased PKA activity. The decreased PKA activity in turn relieves the inhibitory effect of PKA on c-Raf, thus potentiating the c-Raf/MEK/ERK signaling. Both the Gαq subunit and Gβγ subunit, which is dissociated from both Gi and Gq following FFAR1 activation, contribute to ERK phosphorylation, although the signaling pathway does not involve PLC-β, PKC, or Src. Gi-coupled FFAR1 also activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, which is mediated through Gαi/ras/Src signaling. The MEK/ERK pathway directly induces cell proliferation, and the PI3K/Akt pathway induces p70S6K phosphorylation via mTORC1. The MEK/ERK pathway also cross activates mTORC1 and induces phosphorylation of p70S6K. p70S6K phosphorylates S6 ribosomal protein and leads to HASM cell proliferation.