Fig. 2.
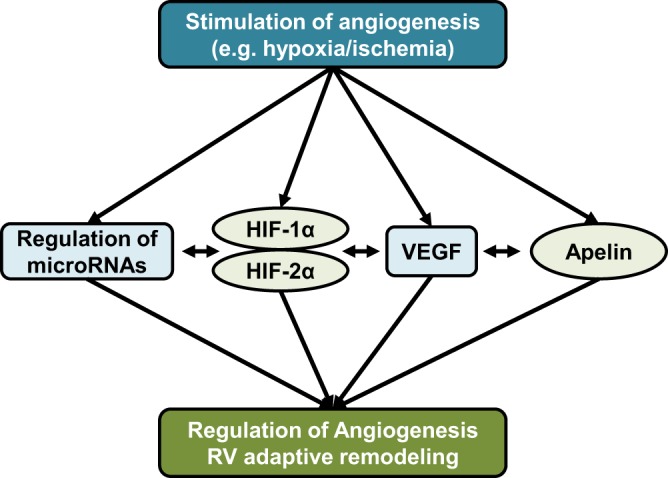
Simplified schematic of currently known pathways regulating angiogenesis in the right ventricle (RV). Proangiogenic factors such as hypoxia or ischemia increase activation and/or abundance of proangiogenic mediators such as hypoxia-inducible factors, VEGF, apelin, and micro-RNAs. Significant cross-talk exists between angiogenic pathways. For example, hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are master regulators that regulate the expression of other regulators to induce angiogenesis during adaptive remodeling of the RV. However, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), apelin, and micro-RNAs are likely also activated independently of HIFs. Decreased or insufficient upregulation of proangiogenic pathways, as well as defects in their downstream signaling pathways are purported to contribute to maladaptive RV remodeling and decompensation.
