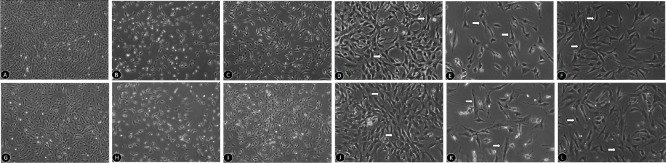
Figure 2.
Morphological changes in Müller cells treated with Y-27632 and exposed to hypoxic or oxidative stress conditions.
(A–F) Morphological changes in Müller cells treated with 10 μM Y-27632 after 24 hours of hypoxia (original magnification: 40× in A–C and 100× in D–F). (A, D) Cellular morphologies in the control group: cells are often long spindle- or triangular-shaped. (B, E) Cellular morphologies in the CoCl2 group: the number of cells is reduced and the shape is irregular. (C, F) Cellular morphologies in the CoCl2 + Y27632 group: cell number increases and shape improves compared with the CoCl2 group. (G–L) Morphological changes in Müller cells treated with 10 μM Y-27632 after 24 hours of oxidative stress (original magnification: 40× in G–I and 100× in J–L). (G, I) Cellular morphologies in the control group. (H, K) Cellular morphologies in the H2O2 group. (I, L) Cellular morphologies in the H2O2 + Y27632 group. Arrows indicate Müller cells.