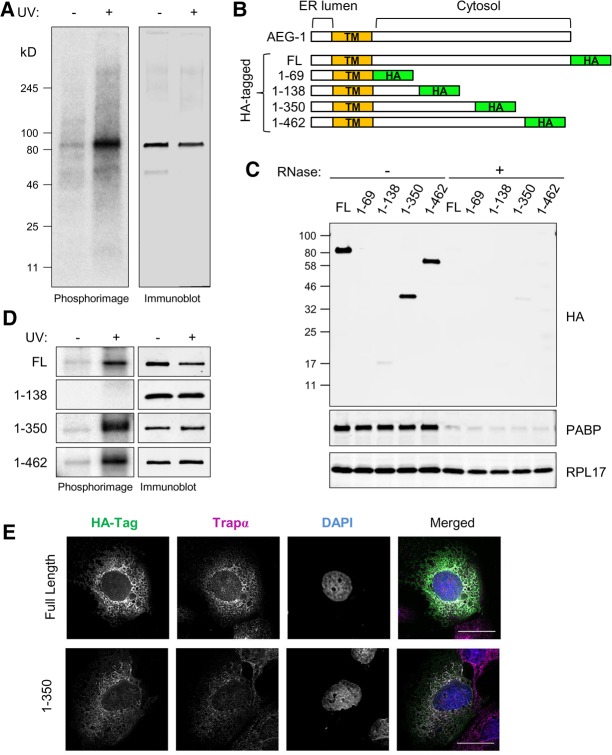
FIGURE 3.
Mutagenic domain mapping of AEG-1–RNA interaction. (A) Endogenous AEG-1 can be crosslinked to RNA in living cells. Cells were UV-irradiated and processed as described in the legend to Figure 1, using antibodies directed against native AEG-1. Depicted is a phosphorimage of the radiolabeled anti-AEG-1 immunoprecipitates and paired immunoblots in control (−UV) and experimental (+UV) conditions. (B) Schematic illustration of AEG-1 deletion mutants. HA-tagged full length (FL) and four C-terminal deletion mutants are shown. (TM) Transmembrane domain. (C) Immunoblot analysis of HA-tagged AEG-1 mutants, poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), and ribosomal protein (RPL17) in pellet fractions derived from ultracentrifugation analyses with/without RNase digestion. (D) Phosphorimager images depicting radiolabeled protein–RNA complex formation of AEG-1 mutants +/− UV crosslinking (left panels). Immunoblot analysis of HA-tagged AEG-1 truncation mutants +/− UV crosslinking, demonstrating recovery of HA-tagged AEG-1 forms in both fractions. (E) Immunofluorescence micrographs of full length (AEG-1) and truncation mutants illustrating ER localization of C-terminal truncated forms. Scale bar, 25 µm.