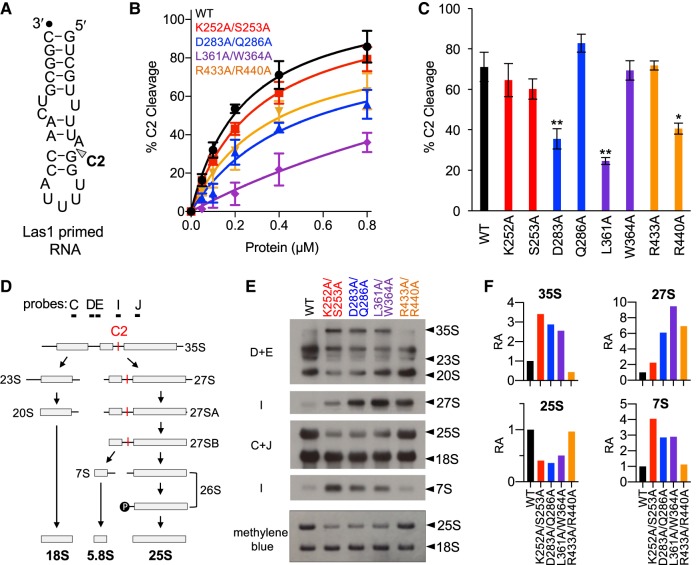
FIGURE 10.
PNK active site motifs facilitate Grc3/Las1 crosstalk in vitro and in vivo. (A) S. cerevisiae ITS2 model RNA substrate. C2 cleavage site is marked by an arrowhead. Black dot marks the 3′-end labeled fluorophore. (B) C2 RNA cleavage by Las1 bound to Grc3 PNK variants. A protein concentration series (0–0.8 µM) of Grc3/Las1 WT and PNK variants (P-loop [K252A/S253A], Walker B [D283A/Q286A], Clasp [L361A/W364A], and Lid [R433A, R440A]) were incubated with 0.1 µM fluorescently labeled Las1 primed RNA. (C) Quantification of C2 RNA cleavage by Grc3/Las1 variants (0.8 µM) incubated with 0.1 µM Las1 primed RNA. (*) P < 0.01; (**) P < 0.005 were calculated by a two-tailed Student's t-test. (D) Simplified S. cerevisiae pre-rRNA processing pathway. The C2 site (red) and probes are marked on the S. cerevisiae pre-rRNA processing pathway. (E) Northern blot analysis of tetO7-GRC3 transformed with plasmids encoding Grc3 PNK active site motif mutants (P-loop [K252A/S253A], Walker B [D283A/Q286A], Clasp [L361A/W364A], and Lid [R433A, R440A]). RNA loading was monitored by methylene blue staining. (F) The integrative density of rRNA was normalized to the mature 18S rRNA. Relative abundance (RA) of pre-rRNA intermediates was calculated by dividing the integrative density of rRNA to the equivalent rRNA from the wild-type strain. Quantification of rRNA intermediates was calculated from a single representative northern blot presented in panel E.