FIGURE 3.
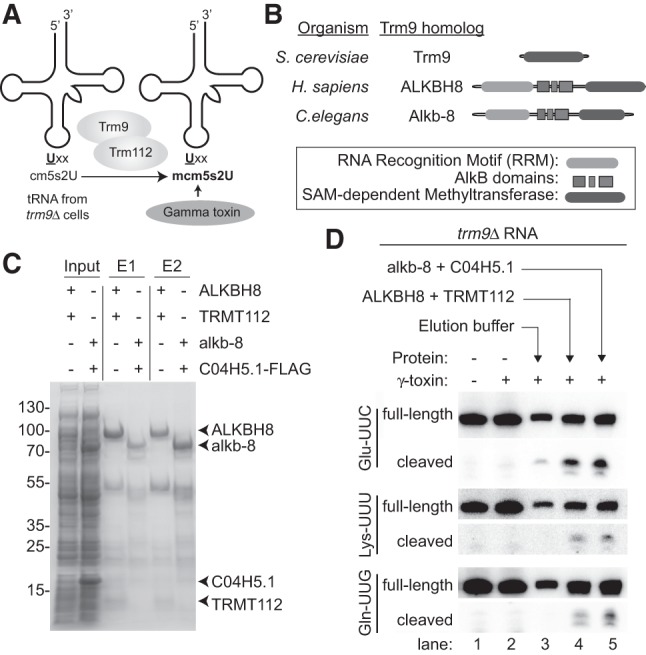
Using the γ-toxin assay to validate the biochemical activity of putative Trm9–Trm112 homologs. (A) Schematic of γ-toxin assay to characterize Trm9–Trm112 enzymes for methyltransferase activity. The tRNA of S. cerevisiae trm9Δ strains lack the mcm5s2U modification and instead harbors the cm5U modification that can be methylated in vitro by purified Trm9–Trm112 enzyme complexes. Formation of mcm5s2U can be subsequently detected by the γ-toxin assay. (B) Schematic of S. cerevisiae Trm9p along with the H. sapiens and C. elegans homologs, ALKBH8 and Alkb-8, respectively. Both human and C. elegans homologs contain a SAM-dependent methyltransferase domain in addition to a RNA recognition motif (RRM) and AlkB dioxygenase domain. (C) Purified protein expressed in E. coli cells along with cellular inputs were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie stain. Arrows denote respective proteins. (D) Total RNA extracted from the yeast trm9Δ line was incubated with either elution buffer, human ALKBH8–TRMT112, or C. elegans alkb-8-C04H5.1 and then subjected to the γ-toxin assay.
