Figure 4.
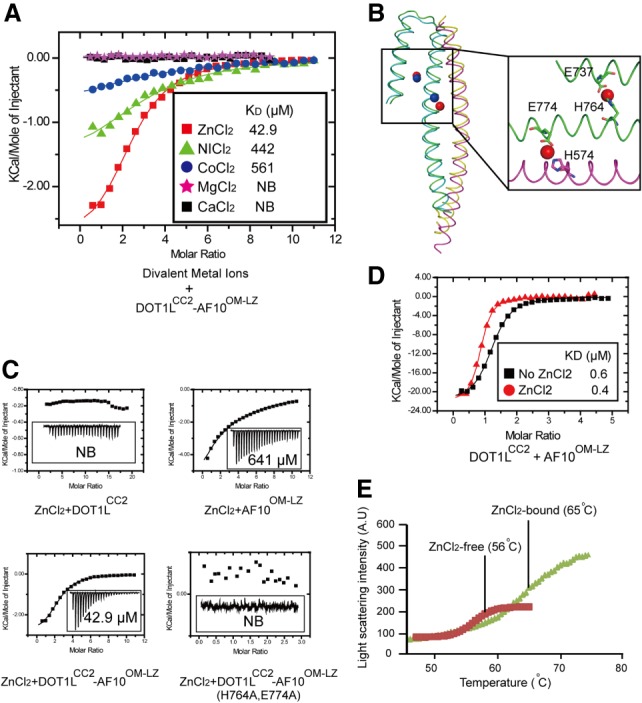
Zinc enhances the binding ability of DOT1LCC2 to AF10OM-LZ. (A) Summary of the quantitative binding constants between various divalent metal ions and the DOT1LCC2–AF10OM-LZ complex. (B) There are two conserved zinc-binding sites in the DOT1LCC2–AF10OM-LZ complex. (C) Dissociation constants of zinc with DOT1LCC2, AF10OM-LZ, and the DOT1LCC2–AF10OM-LZ complex. Mutation of zinc-coordinating residues (AF10H764A/E774A) abolishes the zinc binding. (D) ITC data show that zinc enhances the binding of DOT1LCC2 to AF10OM-LZ. (E) The thermal shift melting curves of the DOT1LCC2–AF10OM-LZ complex in the presence or absence of zinc measured by differential static light scattering.
