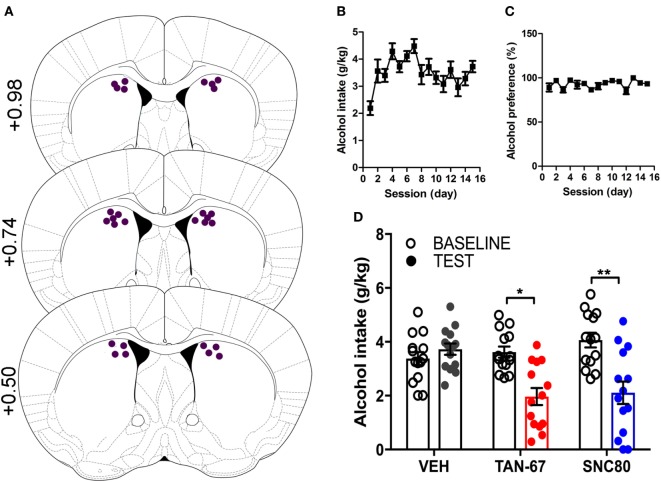
Figure 5.
Genetic knockout (KO) of β-arrestin-2 reveals critical role of Gi/o signaling in reducing alcohol intake via dorsal striatal delta-opioid receptor activation. Cannula placement was verified for all animals included in behavioral analysis (A). C57BL/6 male, β-arrestin-2 KO mice (n = 12) were trained to consume 10% alcohol over the course of 3 weeks, during which they increased their alcohol intake (B) and alcohol preference (C). Vehicle saline (0.9%) infusion did not change alcohol intake, but both TAN-67 and SNC80 (10 µM) significantly decreased alcohol intake (D). Significance by repeated measures, multiple comparisons (Tukey) by two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.