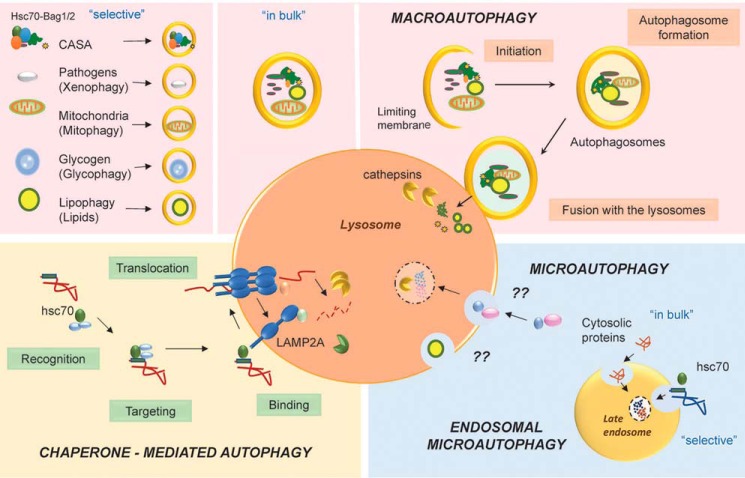
Figure 1.
CMA and eMI in the context of mammalian autophagic pathways. In macroautophagy, cargo (proteins and organelles) sequestered inside autophagosomes in bulk (non selective macroautophagy) or selectively (left) is then delivered to lysosomes through autophagosome/lysosome fusion. In CMA all cargo (proteins) are selectively delivered to lysosomes upon recognition by hsc70 and targeting and binding to the lysosomal membrane protein LAMP2A. Microautophagy requires invagination of the lysosomal membrane to degrade cytosolic material. Proteins and organelles can also be targeted to late endosomes for degradation in mammals through what is known as endosomal microautophagy. Whether mammalian cells are able to directly invaginate the lysosomal membrane to trap cytosolic cargo, as described in yeast, remains unknown (??). CASA, chaperone-assisted selective autophagy.