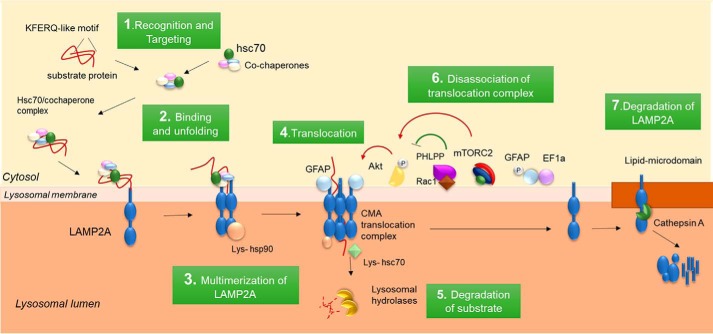
Figure 2.
Steps and lysosomal membrane components of CMA. Proteins degraded through CMA are recognized by hsc70 in the cytosol (step 1) and are targeted to the lysosomal membrane where they bind to LAMP2A (step 2). Substrate binding triggers multimerization of LAMP2A (step 3) to form the complex that mediates substrate translocation (step 4). hsp90 stabilizes LAMP2A through this transition, and luminal hsc70 assists with the internalization of the substrate that then is rapidly degraded by lysosomal proteases (step 5). The stability of LAMP2A in the translocation complex is regulated by the depicted subset of proteins. Once substrate translocate, LAMP2A, dissociates into monomers (step 6). Changes in the turnover of LAMP2A at the lysosomal membrane also contribute to modulate CMA activity (step 7).