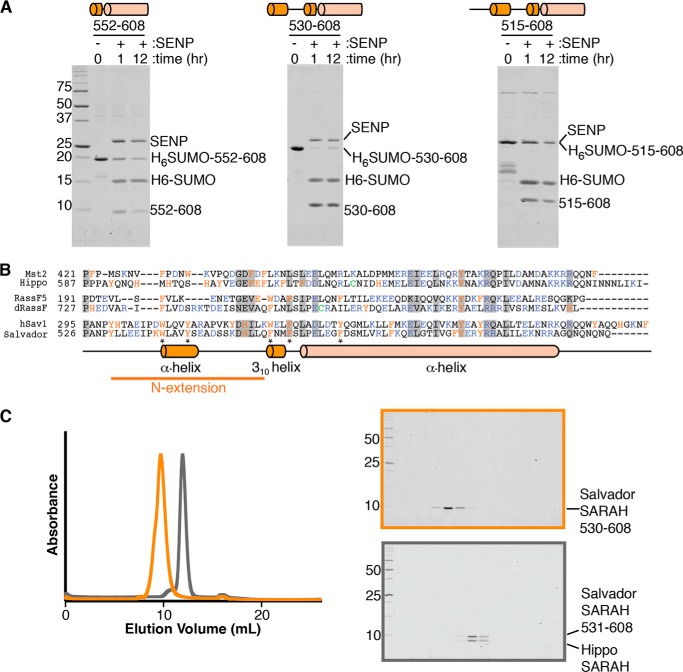
Figure 1.
Additional residues are needed for the solubility of Salvador SARAH domain. A, three His6-SUMO tagged Salvador SARAH domain variants, corresponding to residues 552–608, 530–608, and 515–608, were purified by IMAC. Eluted proteins were incubated with SENP at 4 °C for 1 or 12 h and then separated by Coommassie-stained SDS-PAGE. SENP and tagged His6-SUMO-Salvador SARAH (residues 515–608) migrate at the same position on the gel. The experiment was performed three times and three panels cropped from the same representative gel are shown. A schematic corresponding to the variant used is shown above each panel. B, sequence alignments of the SARAH domains and N-terminal regions of human Mst2, RassF5, and Salvador (hSav1) as well as D. melanogaster Hippo, dRassF, and Salvador. Residues conserved among all six sequences are marked with a gray box. Aromatic residues are colored orange, charged residues purple, and cysteines green. Aligned below is a diagram of the secondary structure assignments derived from the crystal structure for Salvador SARAH domain. Residues that mediate sequence-specific interactions between Hippo and the N-terminal extension of Salvador are indicated by an asterisk. C, left panel are overlaid gel filtration chromatograms of either the Salvador SARAH domain (residues 530–608) (orange) or Salvador–Hippo SARAH (residues 531–608 and 606–662, respectively) (gray). Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE for Salvador SARAH is highlighted in orange (top right) and Salvador–Hippo SARAH in gray (bottom right). Both gels contain fractions spanning from the void volume to the end of the column, and lanes with protein correspond to the peaks on the chromatograms.