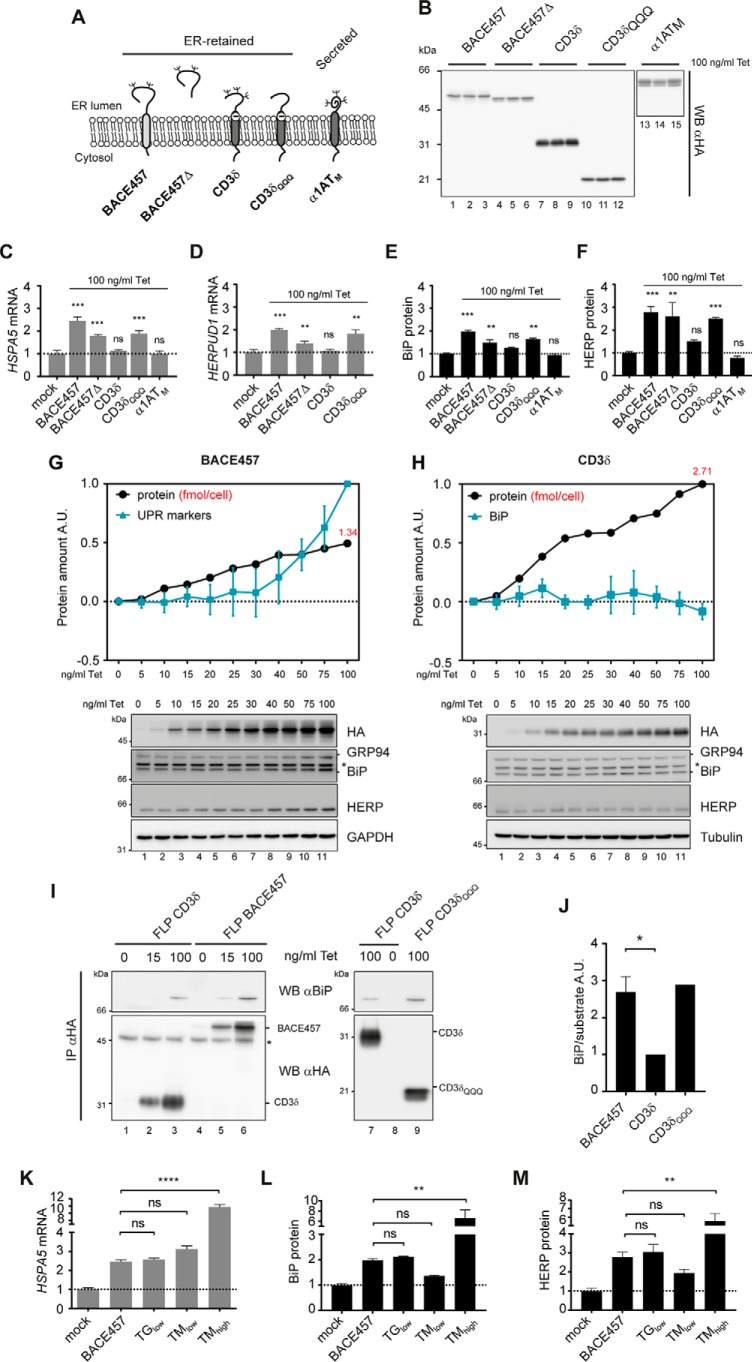
Figure 1.
ER retention and BiP binding are requisite for UPR induction. A, panel of model proteins expressed by inducible HEK293 cells used in this study. B, Western blot (WB) showing the expression level of model proteins on induction with 100 ng/ml of tetracycline. Loadings were normalized based total protein concentration. C, BiP mRNA up-regulation upon 17 h induction of the different model proteins with 100 ng/ml of tetracycline. Mean ± S.E., n = 3, ***, p < 0.001, nonspecific (ns), p > 0.5, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test for multiple comparisons. D, same as C for HERP mRNA. E, BiP protein up-regulation upon 17 h induction of the different model proteins with 100 ng/ml of tetracycline quantified by Western blot. Mean ± S.E., n = 3, ***, p < 0.001, ns, p > 0.5, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test for multiple comparisons. F, same as D for HERP. G, Western blot showing tunable expression of BACE457-HA and progressive induction of UPR markers GRP94, BiP, and HERP. * indicates unspecific, cross-reactive band. In the quantification the blue line is calculated as the average fold-change of the three UPR markers ± S.E. H same as F for CD3δ, which does not induce UPR. I, BiP co-precipitation with unfolded proteins. * indicates anti-HA heavy chain. J, quantification of H. Mean ± S.E., n = 3, *, p < 0.05, BootsRatio (68). K, same as C for drug treatments. ****, p < 0.0001. BACE457 as reference. L, same as E for drug treatments. **, p < 0.01. BACE457 as reference. M same as F for drug treatments. **, p < 0.01. BACE457 as reference.