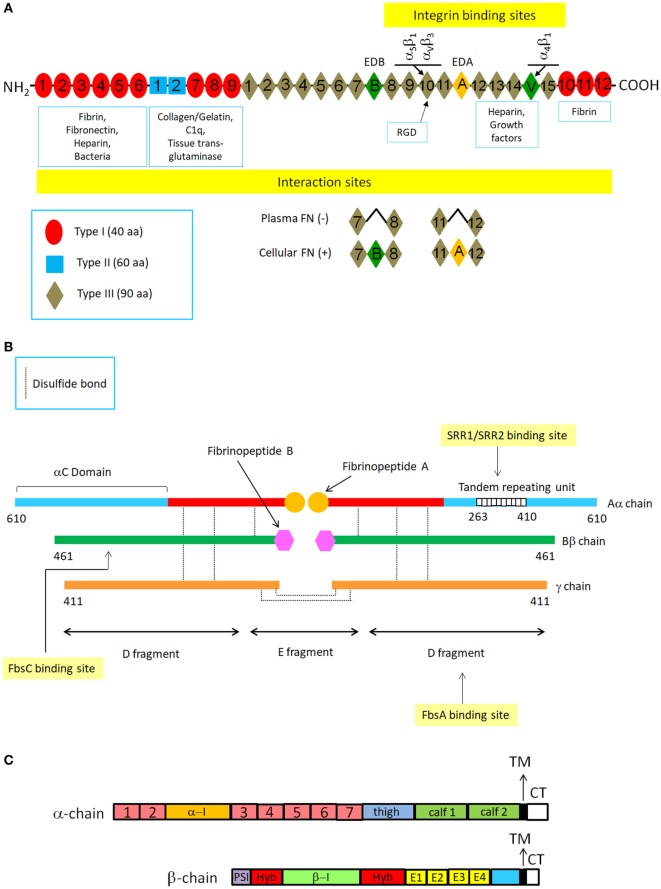
Figure 1.
Schematic structures of typical extracellular matrix proteins fibronectin and fibrinogen and cell surface integrins. (A) Fibronectin (Fn) structure. The drawing shows a representation of a plasma and cellular Fn dimer and its interaction with specific ligands. Fn is a large C-terminally disulfide linked heterodimer. In each monomer there are 12 type I repeats clustered in three groups, two adjacent type II repeats and 15–17 type III repeats. Type I, II, and III repeats consist of 40, 60, and 90 amino acids, respectively. Type I and type II repeats have a specific conformation maintained by pairs of intramodule disulfide bonds, whereas the type III repeat lacks disulfide bonds. The variation in subunit size arises from alternative splicing of three segments: two type III repeats (EDA and EDB) and a third non-homologous segment known as V (variable) or IIICS. Numbering of type III homologies does not include EDA and EDB subdomains. Constitutive sequence RGD within the tenth FnIII module is indicated together with its integrin receptors. (B) Fibrinogen structure. FBG molecule is composed of two halves of disulfide-bridged Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-chains. Each half contains two outer globular D domains, comprising the C-terminal residues of the α-, β-, and γ−chains and connected to a central E domain by a coiled-coil segment. Fibrin formation from FBG starts following thrombin cleavage of fibrinopeptide A from Aα chains. Binding sites on FBG chains or domains for some CWA are also shown. (C) Integrin structure. Integrins are heterodimers composed of α and β chains, each containing around 1,000 and 750 aa, respectively. The α chain contains four/five extracellular domains: a seven bladed β-propeller, a thigh and two calf domains. Some α chains have a α-I domain inserted between the second and the third of the seven blades of the β propeller. The β chain has seven domains: a β-I domain (β-I) is inserted in a hybrid domain (hyb) located immediately after the N-terminal plexin-semaphorin integrin (PSI) domain. These domains are followed by four cysteine-rich epidermal growth factor-like motifs (E1-E4) and a β-tail domain. Both the α and β chains have single transmembrane segments (TM) and short unstructured cytoplasmic tails (CT) that vary in length. Although evidence has been obtained that several CWA proteins such as ACP interact with integrins, molecular details of these interactions have not been produced yet.