Figure 2.
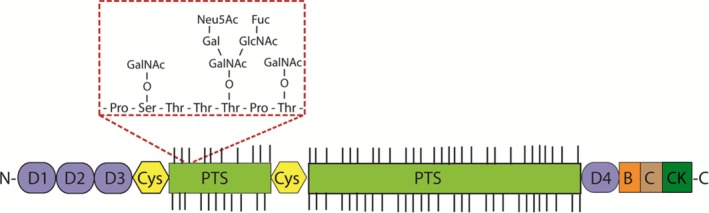
Schematic illustration of the protein domain structure of the polymeric mucin, Muc2. Muc2 consists of cysteine‐rich N‐ and C‐terminal regions. The N‐terminal region is comprised of 3 von Willebrand factor D‐domains (vWf D1‐3), and the C‐terminal domain is comprised of a vWf D‐domain (D4), a vWf B‐ and C‐domain, and a cysteine knot (CK). These terminal regions are involved in mucin polymer formation. The central heavily O‐glycosylated PTS domain is interrupted by a cysteine‐rich region (Cys‐domain). The red box highlights the glycan chains that are added onto the serine and threonine residues within the PTS domain: GalNAc (N‐acetylgalactosamine), Gal (galactose), GlcNAc (N‐acetylglucosamine), Fuc (fucose) and Neu5Ac (sialic acid)
