Figure 2.
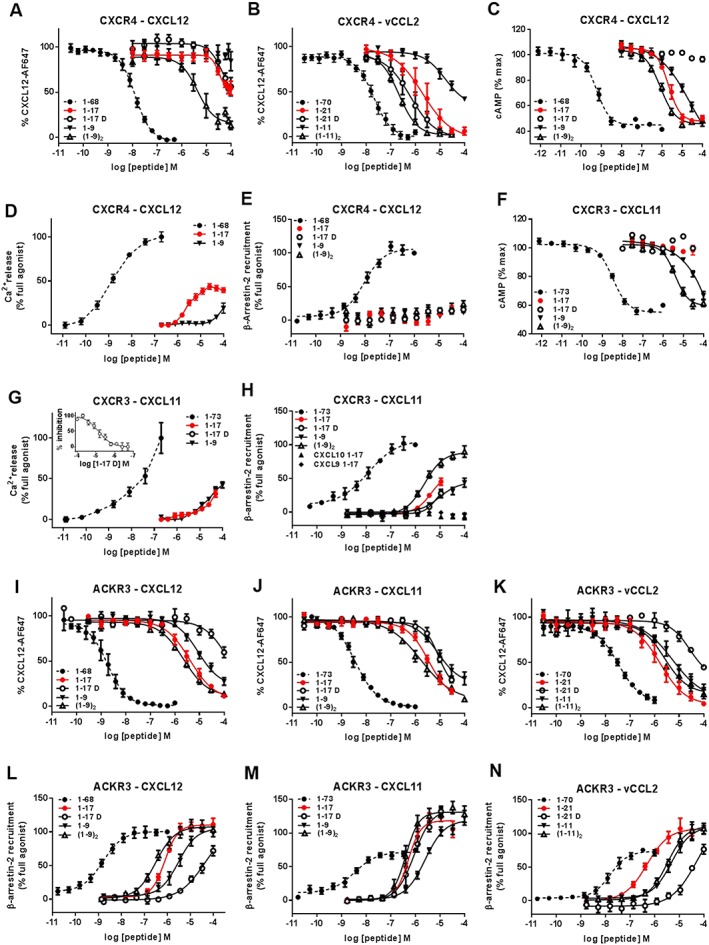
Binding, G protein signalling and β‐arrestin‐2 recruitment to CXCR4, CXCR3 and ACKR3 induced by full‐length chemokines and chemokine N‐terminal peptides. Binding and modulation of CXCR4 (A–E), CXCR3 (F–H) and ACKR3 (I–N) by full‐length CXCL12, CXCL11, vCCL2 and peptides derived from their N‐terminal regions. Binding to CXCR4 (A and B) and ACKR3 (I–K) was assessed by binding competition studies with Alexa Fluor 647‐coupled CXCL12 in U87 cells stably expressing the receptors and analysed by flow cytometry. G protein signalling induced by full‐length chemokines and peptides derived from their N‐terminal regions towards CXCR4 (C and D) and CXCR3 (F and G) was evaluated by measuring the modulation of the basal intracellular cAMP concentration using Glo‐cAMP sensor (C and F) or the release of intracellular calcium using Fluo‐2 dye and FLIPR platform (D and G). (G‐inset) Antagonist properties of peptide CXCL111–17D monitored in calcium assay. β‐arrestin‐2 recruitment to CXCR4 (E), CXCR3 (H) and ACKR3 (L–N) induced by full‐length chemokines and N‐terminal peptides was monitored using a Nanoluciferase‐based complementation assay (NanoBIT). Each experiment was performed five times, and the data shown are means ± SEM.
