Figure 9.
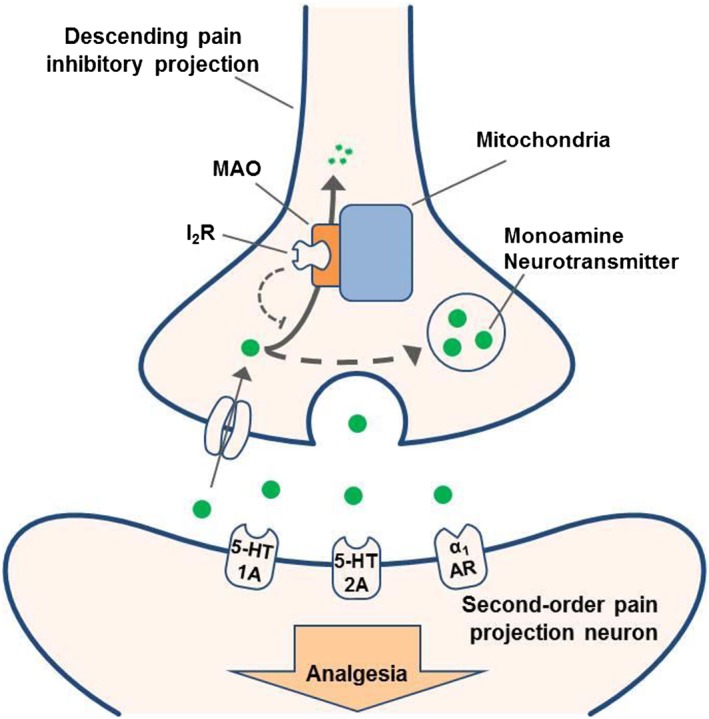
Diagram describing the probable mechanism of action of I2 receptor agonists. Under normal conditions, monoamines such as 5‐HT and noradrenaline undergo reuptake and are metabolized by MAO enzymes (solid arrow). Administration of I2 receptor agonists, and I2 receptor activation, inhibits MAO activity and allows monoamine neurotransmitters to be repackaged, increasing their synaptic concentration (dashed arrows). The corresponding increased activation of certain downstream monoaminergic receptors (i.e. 5‐HT1A, 5‐HT2A and α1‐adrenoceptors) leads to the production of analgesia.
