Figure 3.
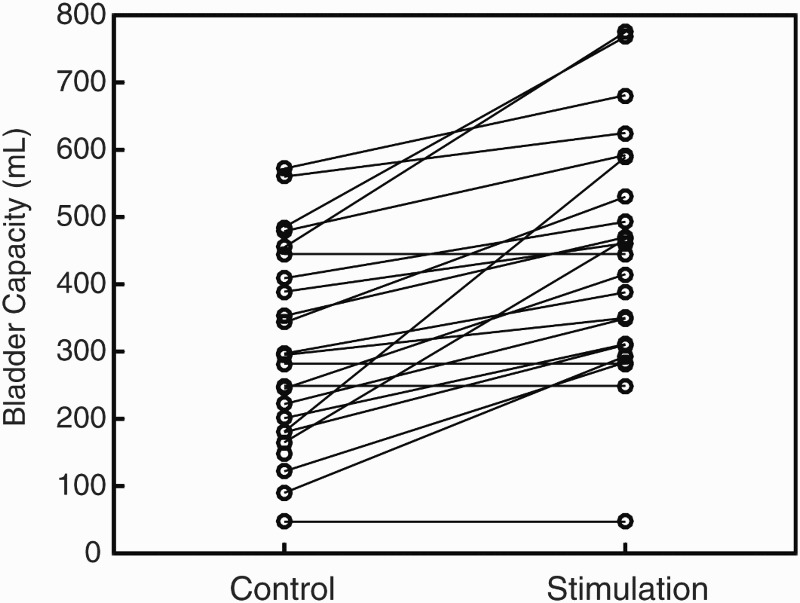
GNS increased bladder capacity and was effective at tolerable stimulation amplitudes. Responses are shown for 23 individual subjects. GNS significantly increased bladder capacities by 135±109 mL from 307 mL (control) to 442 mL (stimulation) (n=23). Bladder capacities increased in 19 of 23 subjects. GNS inhibited acute bladder contractions, but did not increase bladder capacity in four subjects.
