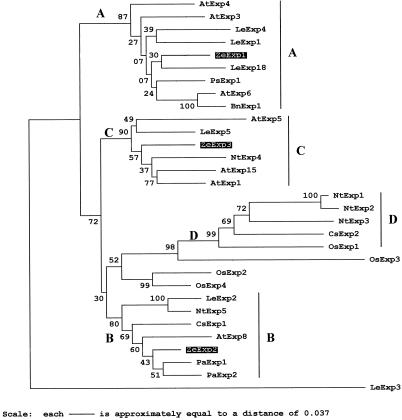
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of 32 α-expansin protein sequences. Numbers on the tree indicate bootstrap P values. Large letters denote the subfamily groupings previously identified (Link and Cosgrove, 1998). This tree was rooted using LeExp3 (Lycopersicon esculentum). Sequences and GenBank accession numbers: AtExp1 (U30476), AtExp2 (U30481), AtExp3 (AC004684), AtExp4 (AC003674), AtExp5 (U30478), AtExp6 (U30480), AtExp8 (AC002336); LeExp1 (U82123), LeExp2 (AF096776), LeExp3 (AF059487), LeExp4 (AF059488), LeExp5 (AF059489), and LeExp18 (AJ004997); Nt (Nicotiana tabacum) Exp1 (AF049350), NtExp2 (AF049351), NtExp3 (AF049352), NtExp4 (AF049353), and NtExp5 (AF049354); Os (Oryza sativa) Exp1 (Y07782), OsExp2 (U30477), OsExp3 (U30479), and OsExp4 (U85246); Ps (Pisum sativa) Exp1 (X85187); Bn (Brassica napus) Exp1 (AJ000885); Cs (Cucumis sativus) Exp1 (U30382), and CsExp2 (U30460); Pa (Prunus armeniaca) Exp1 (U93167) and PaExp2 (AF038815). The 21- and 19-amino acid signal peptides were predicted for the ZeExp2 and ZeExp3, respectively, by the method of von Heijne (1986). Mature proteins were aligned with the CLUSTAL algorithm, and γ-corrected distances between amino acid sequences were used to construct this tree by nearest-neighboring joining using the MEGA program (Kumar et al., 1993).