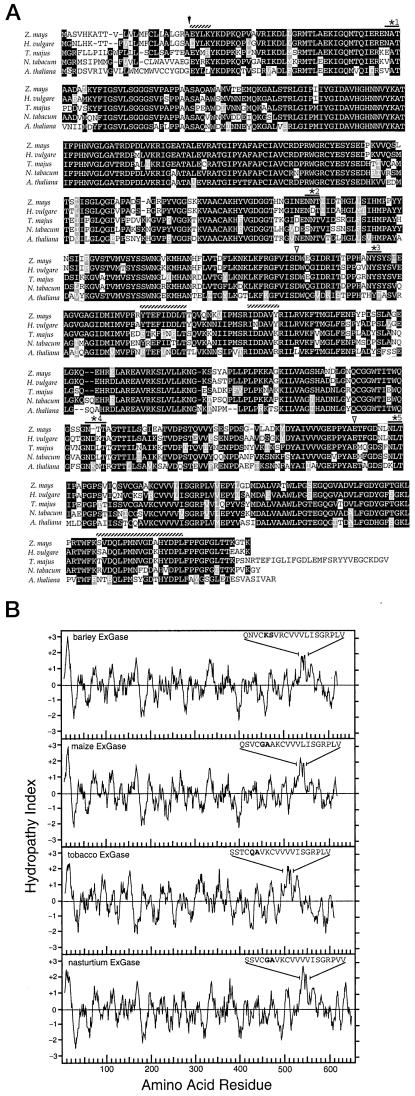
Figure 3.
Comparison of the amino acid sequence and hydropathy indices of the maize, barley, nasturtium, tobacco, and Arabidopsis ExGases. A, The predicted cleavage site of the signal peptide is marked by the black arrow, the sequences of the four tryptic peptides are marked with hatched lines, and the five potential glycosylation sites are starred. The predicted nucleophiles Asp-285 and Glu-492 are marked with white arrows. Whereas the maize ExGase shares potential glycosylation sites 1, 3, and 5 with the barley ExGase HVU46003, it shares only sites 2 and 5 with a barley isoform with the glycosylation sites confirmed by three-dimensional structure (Varghese et al., 1999). B, The hydropathy plots were calculated according to the Kyte-Doolittle parameters with an amino acid range of 11. The sequences of amino acids 531 through 550 for barley ExGase (24; HVU46003) and 529 through 548 for the maize ExGase show the substitution of Gly-533 and Ala-534 in the maize enzyme for Lys-535 and Ser-536 for the barley enzyme in bold. Sequences 496 through 515 encoded by the Arabidopsis homolog (AB008271, clone MUK11) contain Gln-500 and Ala-501, and amino acids 534 through 553 for nasturtium ExGase (AJ006501) contain Gly-538 and Ala-539, in those positions and are also in bold.