FIGURE 2.
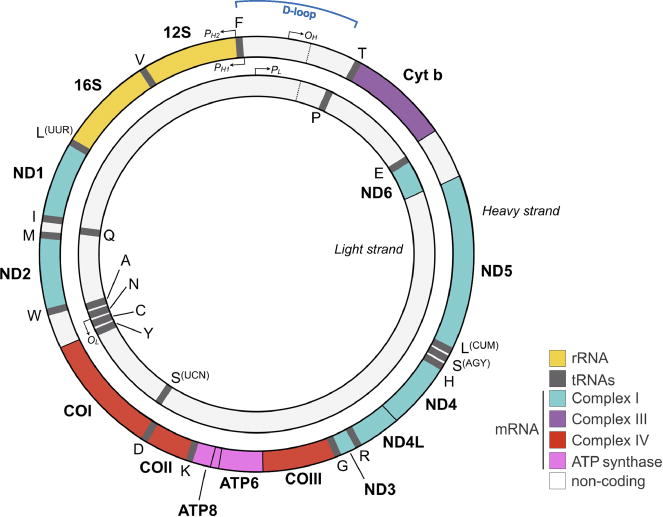
The human mitochondrial genome (mtDNA). The mtDNA contains 16,569 nucleotides and encodes 37 canonical genes, including 2 rRNA and 22 tRNA required for protein synthesis. Encoded proteins constitute part of the respiratory chain and include seven subunits of complex I, one subunit of complex III, three subunits of complex IV, and two subunits of complex V. Other mtDNA-encoded mRNA transcripts giving rise to secreted mitokines have also been described (28). The mtDNA is composed of light (inner circle) and heavy (outer circle) mtDNA strands. The mtDNA is replicated from two origins of replication on the light and heavy strands termed OL and OH, respectively. mtDNA gene expression is initiated from promoters on the heavy strand (PH1 and PH2) and on the light strand (PL). The glucocorticoid receptor and other transcription factors interact with the mtDNA near the D-loop (29). Ethnic differences exist in mtDNA sequence (31,32). Note that colors for each gene are matched to the respiratory chain complexes, of which they encode a subunit in Figure 1. mtDNA = mitochondrial DNA; rRNA = ribosomal RNA; tRNA = transfer RNA; mRNA = messenger RNA; ATP = adenosine triphosphate. Color image is available only in online version (www.psychosomaticmedicine.org).
