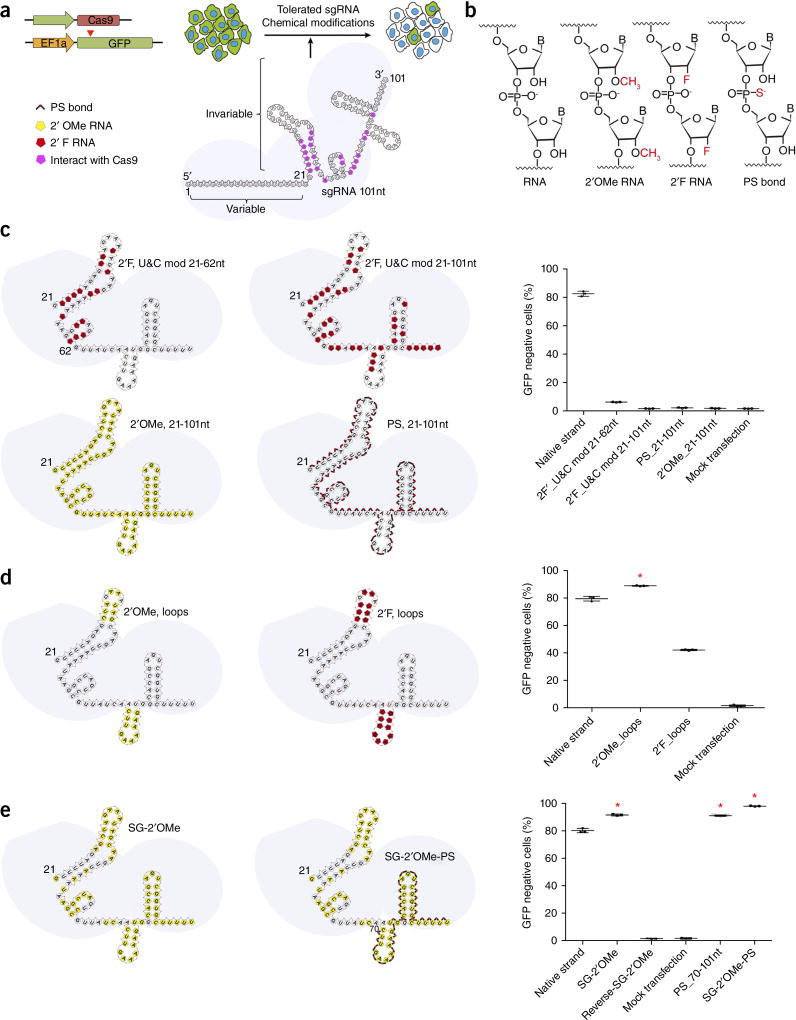
Figure 1.
Chemical modifications of invariable part of sgRNA. (a) HEK293 cells stably expressing both EF1a promoter-GFP and EFs promoter-spCas9 were incubated with a GFP-targeting sgRNA. Cas9–sgRNA-mediated frameshift NHEJ will yield GFP− cells. When a pattern of chemical modification is tolerated by Cas9–sgRNA, the % of GFP− cells will be retained. The pink highlighted nucleotides in the invariable region of sgRNA that interact with the Cas9 protein at the 2′ hydroxyl (OH) group. (b) Chemical modifications of RNA used in the study. (c–e) Left: Illustration of full or “U” and “C” chemical modification (c), loops modification (d) and structure-guided modification (e) in the invariable region (Cas9 binding and tail region) of sgRNA. Right: FACS analysis of HEK293 cells described in a incubated with sgRNAs with various modifications and without modification (native strand). *P < 0.05. (n = 3), error bars as s.d.