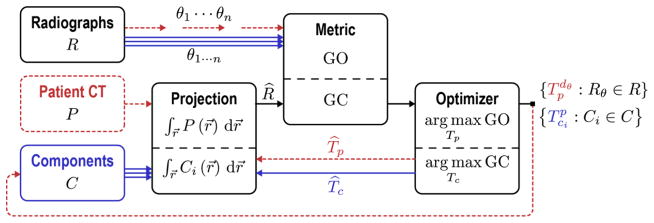
Figure 1.
Flowchart for the Known-Component Registration (KC-Reg) algorithm. Two stages operate in tandem: registration of 2D radiographs (P) acquired at perspective views (θ) to: (i) the 3D patient CT (P) shown by dotted paths; and (ii) the 3D models of surgical components (C) shown by solid paths. The “Projection” is a GPU-accelerated forward projection operation that generates DRRs. The similarity “Metric” is a gradient-based objective function (GO for patient registration and GC for component registration) that is then maximized by the “Optimizer” (CMA-ES). The registration yields transforms T that relate the 3D positions of surgical components within the reference frame of the patient CT, allowing quantitative assessment of the surgical construct.