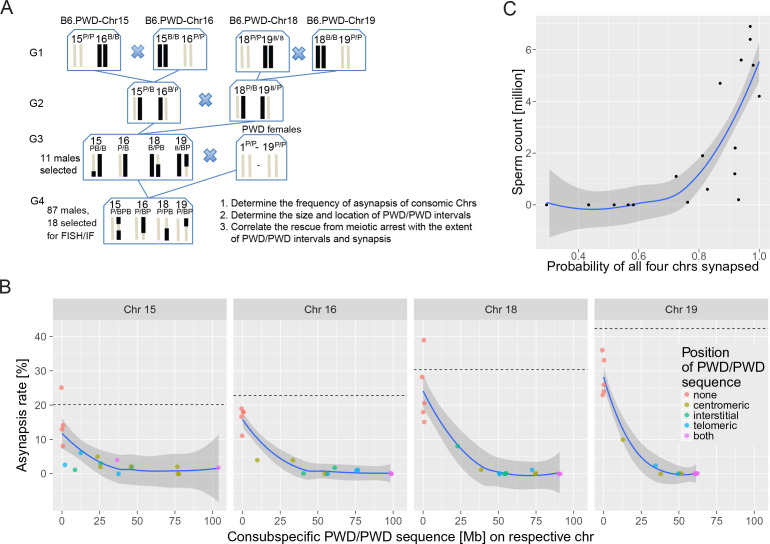
Figure 4. The effect of consubspecific PWD/PWD stretches of genomic sequence on pachytene synapsis and meiotic progression, 4-chr cross.
(A) Scheme of a four-generation cross resulting in F1 hybrids with four recombinant consomic chromosomes. (B) The asynapsis rate related to the size and chromosomal position of the consubspecific PWD/PWD sequence in four consomic chromosomes (15, 16, 18 and 19, see also Figure 4—source data 3). The localization of PWD homozygous sequence with respect to the centromere, the interstitial part of the chromosome, or the telomere, or on both ends is distinguished by color (see also Figure 4—source data 3). (C) Number of sperm in epididymis is a function of the probability of synapsis of all four consomic chromosomes. The complete meiotic arrest is reversed in males having 70% or higher chance of all four chromosomes synapsed. See Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Loess curve with 95% CI.
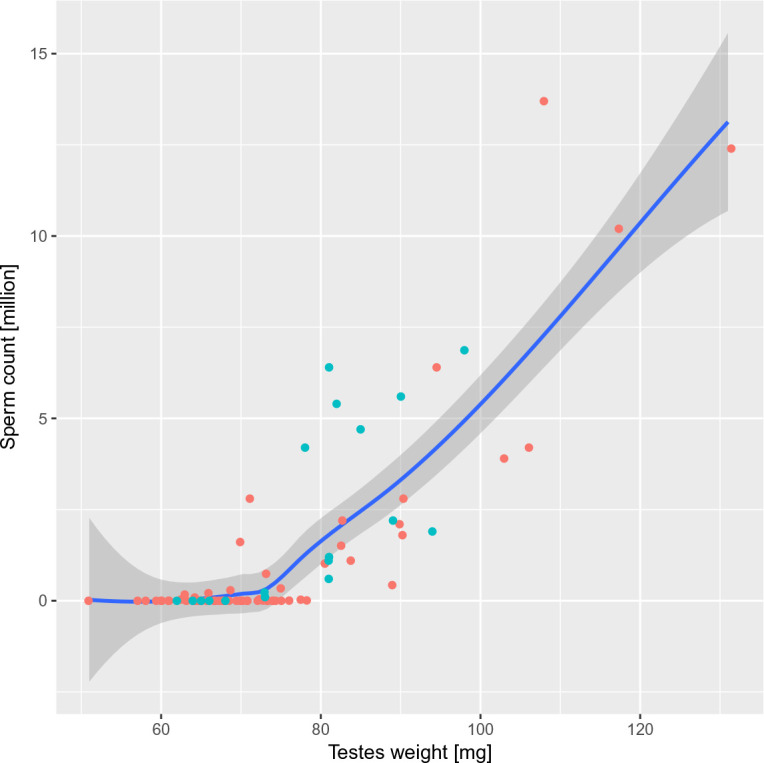
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Fertility parameters of G4 males from the 4-chr cross.