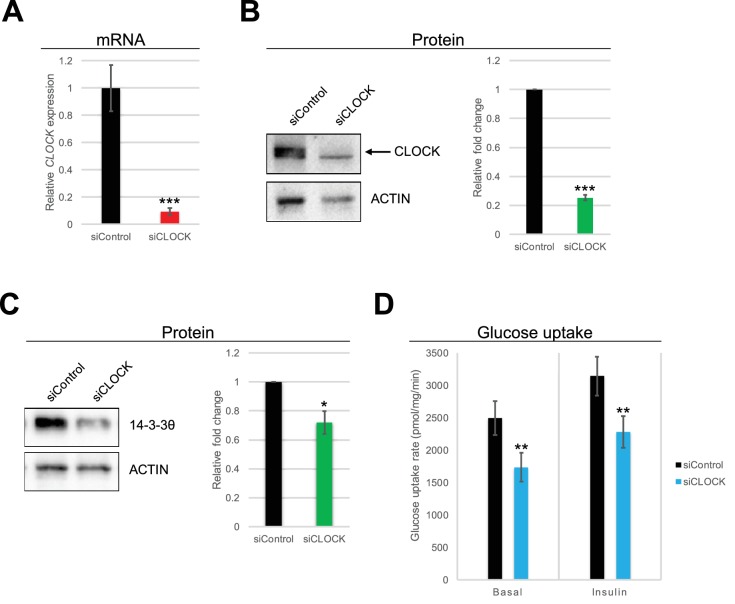
Figure 3. Basal and insulin-induced glucose uptake by hSKM is downregulated in the absence of a functional circadian clock.
(A) CLOCK mRNA was measured in hSKM cells transfected with siControl or siCLOCK by RT-qPCR and normalized to the mean of 9S and HPRT. CLOCK expression was reduced by 91 ± 2% (mean ± SEM, N = 4; (***) p-value <0.001) in siCLOCK-transfected cells. Protein levels of CLOCK (B) and 14-3-3θ (C) were assessed by western blot. Left panel: representative western blot; right panel protein quantification over all monoplicates (mean ± SEM, N = 5). CLOCK and 14-3-3θ protein levels were reduced by 75 ± 2%, and 28 ± 8%, respectively. (D) Glucose uptake rates (in pmol/mg.min) measured in the absence (basal) or presence (insulin) of insulin (1 hr, 100 nM) in siControl or siCLOCK-transfected cells. Note significant reduction of basal (31 ± 3%) and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (28 ± 3%). Data are mean ± SEM of four independent experiments using myotubes from four different donors (same as for A-C). (*) p-value <0.05, (**) p-value <0.01, (***) p-value <0.001.