Figure 2.
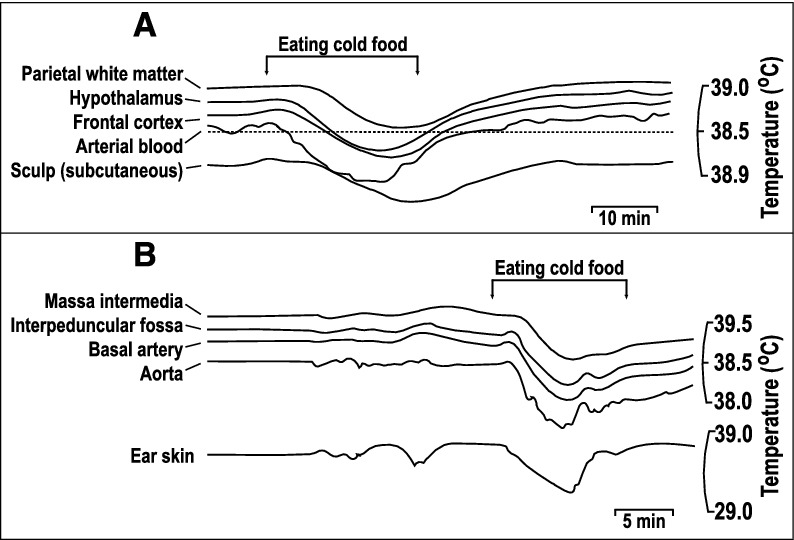
Comparison of brain and arterial blood temperature dynamics during body cooling induced by the consumption of cold food. A. A monkey fills cheek pouches with bananas chilled to 10°C and eats them (arrows). Note that the rapid cooling of arterial blood was followed by cooling of the frontal cortex and hypothalamus with a short delay. In contrast, the parietal subcortical white matter and subcutaneous tissue of the scalp demonstrated significant thermal inertia, as evident from the long delays in the response onset and nadir at each of these locations. B. A rabbit eats cold, chopped apples (arrows). The temperature dynamics in the aorta, basilar artery, and interpeduncular fossa were nearly identical (for clarity, the authors lowered the traces from the aorta and basilar artery), whereas those in the massa intermedia and ear skin were delayed. Replotted from the data reported in ref. [22].
