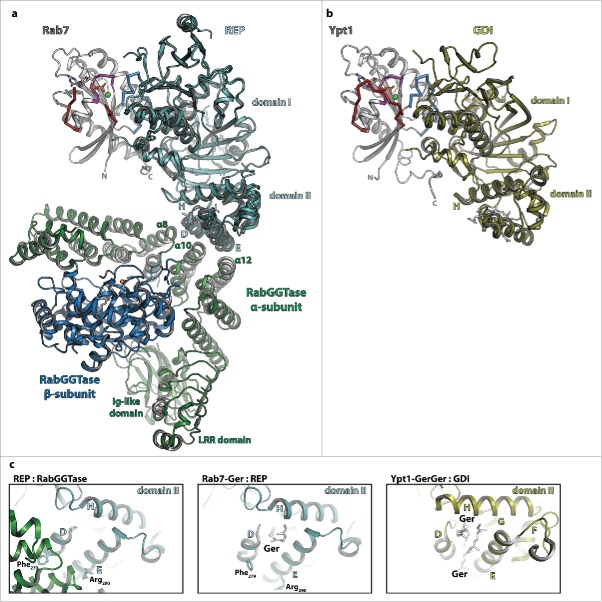
Figure 4.
The interaction of Rab proteins with REP, RabGGTase and GDI. (a) Model of the ternary complex between Rab7:GDP (gray, switch I – red, switch II – blue, P-loop – magenta, Mg2+ - green sphere, GDP - sticks), REP (cyan) and RabGGTase (α-subunit – green, β-subunit – blue, Zn2+ - orange sphere). The ternary complex was modeled from the structures of Rab7:REP (pdb id 1VG0) and REP:RabGGTase (pdb id 1LTX). (b) Model of doubly prenylated Ypt1:GDP (colors as above) in complex with GDI (yellow, pdb id 2BCG). Note the structural similarity between Rab7:REP and Ypt1:GDI. (c) Close-up view of helices D, E and H of the lipid-binding domain II of REP in complex with RabGGTase (left) or in complex with one geranylgeranyl-group (middle) and of the corresponding domain II of GDI in complex with 2 geranylgeranyl-groups (right). A conformational change within this domain upon binding of the C-terminally linked geranylgeranyl-groups of the Rab is presumably the cause of dissociation of RabGGTase from REP subsequent to prenylation.