Figure 7.
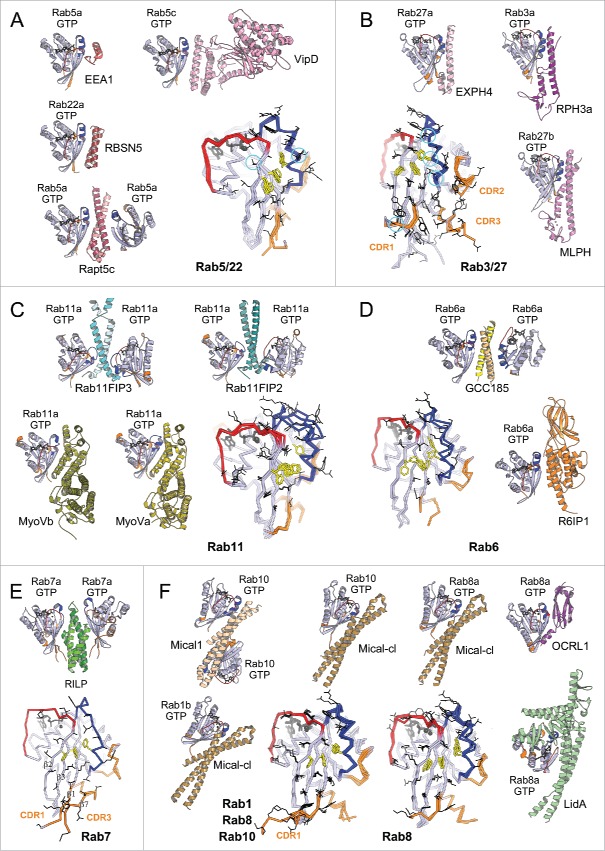
Rab effector binding surface. Structures of Rab-GTP molecules bound to effectors are shown (cartoon) and superimposed (line) to represent their effector binding sites. Residues changing their solvent assessable area upon binding to the effectors are shown in black lines, hydrophobic triad residues are shown in yellow sticks. (A) Rab5/22-effector complexes. Structures of homologous Rab5 and Rab22 bound to their effectors' RBDs, including EEA1-C2H2-RBD (3MJH), Rabaptin5-Cterminal-RBD (Rapt5; 1TU3), Rabenosyn5-(728–784)-RBD (RBSN5; 1Z0J), and VipD (4KYI), are shown. The superimposed structures illustrate that the effector binding site is similar among different Rab-effector interactions. Rab5/22 specific residues contributing to binding specificity are highlighted with cyan circles. (B) Rab3/27-effector complexes: Rab3a/Rabphilin3a-RBD (RPH3a; 1ZBD), Rab27a/Exophilin4-RBD (EXPH4; 3BC1), and Rab27b/Melanophilin-RBD (MLPH; 2ZET). The effector binding site is extended to the CDR1–3 regions. Cyan circles highlight residues that are different between Rab3 and Rab27, contributing to Rab27 selectivity. (C) Rab11a bound to the RBDs of effectors Rab11FIP2 (4C4P), Rab11FIP3 (2HV8), MyosinVa (MyoVa; 5JCZ), and MyosinVb (MyoVb; 4LX0) are shown. The binding site undergoes remodeling in Switch1, Switch2 and the hydrophobic triad. (D) Rab6a binds 2 effectors RBDs, GCC185 (3BBP) and Rab6IP1 (3CWZ), in different conformations. (E) Rab7a binding to RILP-RBD (1YHN) induces remodeling of the C-terminal CDR3 region that forms an additional β-strand (β7). (F) Rab1b, Rab8a and Rab10 interact with Mical-family (Mical-cl and Mical1) (5SZH, 5SZI, 5LPN, 5SZJ) RBDs using similar binding sites except for the CDR1 region, which modulates the partners binding affinities. In the case of Rab8a, complex structures of it bound to different effectors' RBDs, including OCRL1 (3QBT), Mical-cl (5SZI) and LidA (3TNF), demonstrate subtle structural rearrangements in Switch1 and Switch2.