Figure 8.
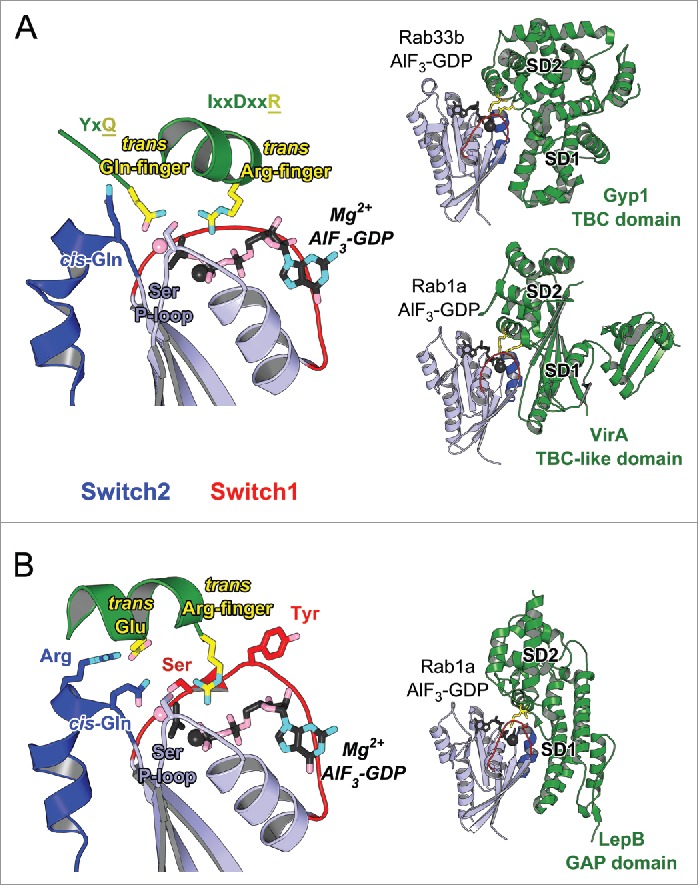
Structures of Rab-GAP complexes and the mechanisms of GAP stimulated GTP hydrolysis. Representative Rab/RabGAP complexes: Rab33b/Gyp1-TBC-domain (2G77), Rab1a/VirA-TBC-like-domain (4FMB), and Rab1a/LepB-GAP-domain (4IRU). (A) TBC domain Gyp1 and bacterial RabGAP VirA have different folds but stimulate Rab GTP hydrolysis using the same, dual trans-finger mechanism exploiting the trans-Gln-finger and trans-Arg-finger from the conserved TBC YxQ and IxxDxxR motifs, respectively. The nucleophilic water is shown as a pink sphere. The cis-Gln in the Rab Switch2 PM3 motif contributes to GAP binding. (B) LepB, a bacterial RabGAP, binds to Rab1a and generates a trans-cis polar network where the GAP supplies the trans-Arg-finger and trans-Glu to the GTPase hydrolytic site and the Rab provides the cis-Gln from the PM3 motif, Ser residues from the P-loop and Switch1, and the Arg from Switch2. The Switch1 Tyr contributes to destabilization of the Rab ground state as well as binding to LepB.
