Figure 9.
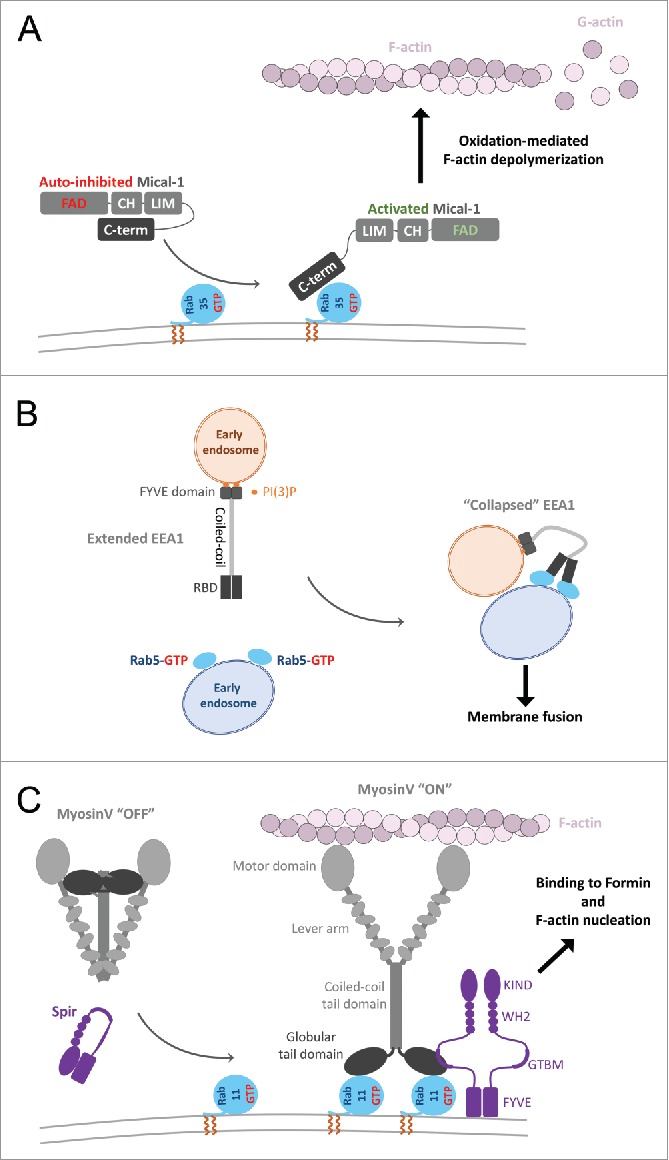
Effector conformational activation. (A) A schematic model of Mical1 activation upon Rab35 binding. Mical1s C-terminal domain, including the RBD, engages in auto-inhibitory interactions with its FAD-CH-LIM domains. Rab35 binding to the C-terminal domain promotes Mical1 enzymatic activity presumably by destabilizing the auto-inhibited state. (B) Dimeric EEA1 associates with early endosomes by binding to PI(3)P with its C-terminal FYVE domain. Its extended coiled-coil allows the N-terminal C2H2Zn2+ RBD to bind to Rab5-GTP, thereby capturing another early endosome. This interaction induces entropic collapse of its coiled-coil region, bringing 2 membranes together before endosomal fusion. (C) Rab11 cooperates with Spir in MyosinV activation and membrane recruitment. Spir and MyoV proteins adopt a back-folded, auto-inhibited conformation in the cytoplasm. Spir's globular tail binding motif (GTBM) binds to the inhibited MyoV and contributes to the release of MyoV auto-inhibition and facilitates MyoV-GTD interaction with Rab11 on vesicles. Together, they stabilize MyoV in an activated, extended conformation on the membrane. Spir's FYVE domain binds to the membrane and the WH2-KIND domains are available for interaction with Formin1 and F-actin nucleation.
