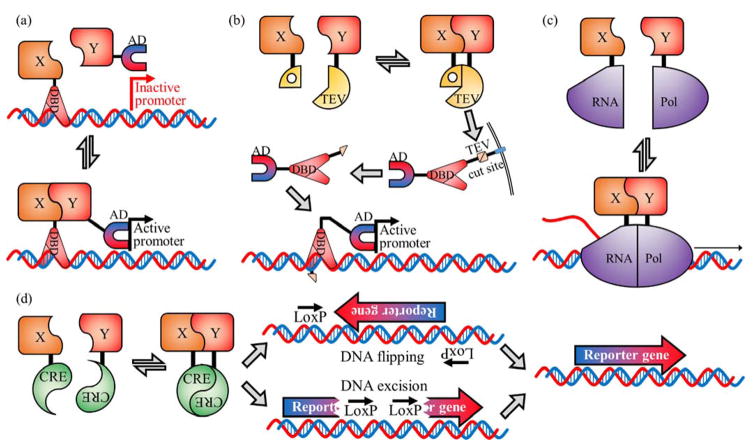
FIGURE 2.
Gene-level control PPi detection systems. (a) Yeast 2-hybrid based on split Gal4.12 The Gal4 transcription factor is split into two parts, the DNA binding domain (DBD) and the activation domain (AD). When fused proteins of interest (X and Y) interact, transcription is initiated and the reporter gene is expressed. (b) Split TEV protease system.13 A transcription factor is tethered to the membrane with a linker containing a TEV protease cut site. The interaction of proteins X and Y leads to reconstitution of TEV protease which cleaves the linker releasing the transcription factor which then activates expression of the reporter gene. (c) Split RNA polymerase.16 The PPi between X and Y brings the two parts of T7 RNA polymerase together allowing transcription of the reporter gene to occur. (d) Split Cre recombinase. Initially the reporter gene is inactive, due to an inverted orientation or an insertion that disables the gene. The interaction of X and Y reconstitutes Cre recombinase which flips the gene, or excises part of the DNA, to enable proper expression of the reporter gene.