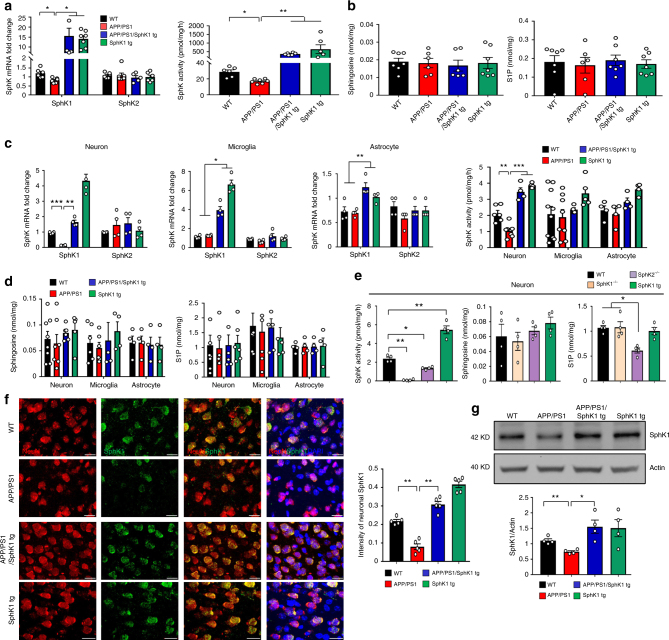
Fig. 1.
SphK1 is decreased in APP/PS1 mice neuron. a SphK1 (n = 6–7 per group) and SphK2 mRNA (n = 5–7 per group) and SphK activity (n = 6–7 per group) in cortex of brain. b Detection of sphingosine (n = 6–7 per group) and S1P (n = 6–7 per group) in brain. c SphK1 and SphK2 mRNA (n = 4 per group) and SphK activity (n = 4–10 per group) in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes isolated from mouse brain. d Detection of sphingosine (n = 4–8 per group) and S1P (n = 4–8 per group) in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes isolated from mouse brain. e Detection of SphK activity, sphingosine and S1P in neurons isolated from WT, SphK1−/−, SphK2−/− and SphK1 tg mouse brain (n = 4 per group). f Left, representative immunofluorescence images of cortex showing SphK1 (green) merged with neuron (NeuN, red). Scale bars, 20 μm. Right, quantification of neuronal SphK1 (n = 5 per group). g Western blotting for SphK1 in neuron isolated from mouse brain (n = 4 per group). All data analysis was performed on 9-month-old mice. a–g One-way analysis of variance, Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All error bars indicate s.e.m.