FIGURE 3.
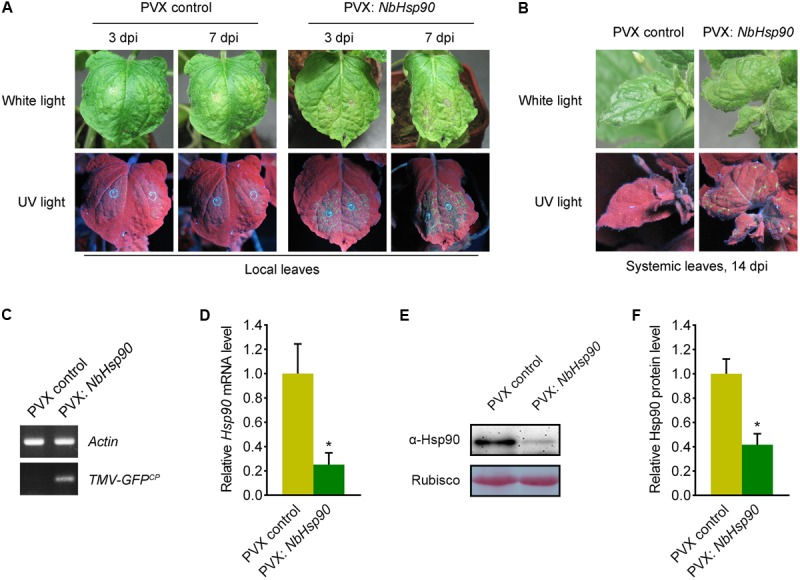
Silencing of NbHsp90 Compromised Tm-22-mediated Resistance to TMV. (A) Silencing of NbHsp90 caused the appearance of TMV-GFP infection foci and visible HR lesions (right) in the inoculated leaves of NbHsp90-silenced Tm-22-containing plants. PVX-infected Tm-22-containing plants were used as negative controls (left). (B) TMV-GFP spread into the systemic leaves of NbHsp90-silenced Tm-22-containing plants (right) but not the PVX control plants (left). Photos were taken at 14 days post TMV-GFP infection (dpi). (C) RT-PCR to confirm the presence of TMV-GFP in systemic leaves of NbHsp90-silenced Tm-22-containing plants (right) but not the PVX control plants (left). (D) Quantitative RT-PCR assays to confirm the reduction in NbHsp90 mRNA (means ± SEM, n = 3). ∗P < 0.05, Student’s t-test. NbActin mRNA levels were used as the internal control. (E,F) Western blot assays to confirm the reduction in NbHsp90 protein level (means ± SEM, n = 4). ∗P < 0.05, Student’s t-test. Equal loading of protein samples was validated by Ponceau Red staining of Rubisco subunit.
