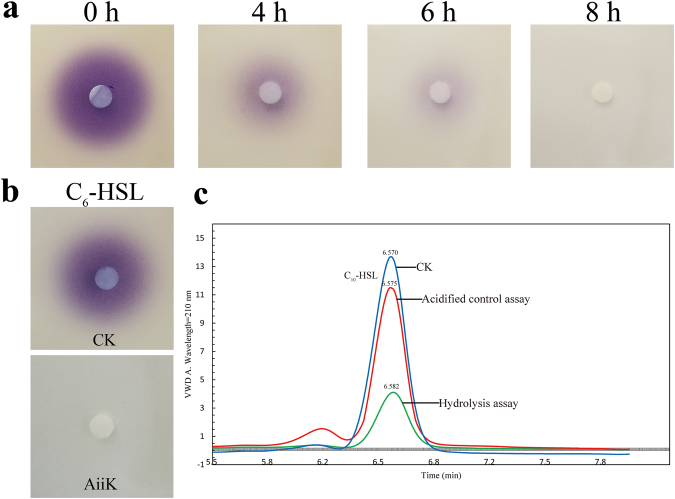
Figure 2.
(a) AHL-degrading activity bioassays in vivo. Subcultures of E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells harboring pET32a-aiiK were mixed with 10 μM C6-HSL and incubated at 37 °C for 0 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, respectively. (b) AHL-degrading activity bioassays in vitro. The purified AiiK (4 μg/mL) were mixed with 10 μM C6-HSL and incubated at 25 °C for 1 h. CK means controls of PBS with the same amount of C6-HSL. The residual AHL was detected using strain C. violaceum CV026. (c) HPLC analysis of C10-HSL degradation. CK means controls of PBS with the same amount of C10-HSL; hydrolysis assay (AiiK: 4 μg/mL, C10-HSL: 50 μM) was carried out at 25 °C for 10 min, and then SDS was used to terminate the reaction; acidified controls assay (AiiK: 4 μg/mL, C10-HSL: 50 μM) was performed at 25 °C for 10 min, and SDS was used to terminate the reaction. The mixture was acidified to pH 2 by adding concentrated HCl and incubated at 25 °C overnight without agitation. The elution time of C10-HSL was at 6.57 ± 0.01 min and C10-HSL was monitored at 210 nm. All experiments were carried out in triplicates.