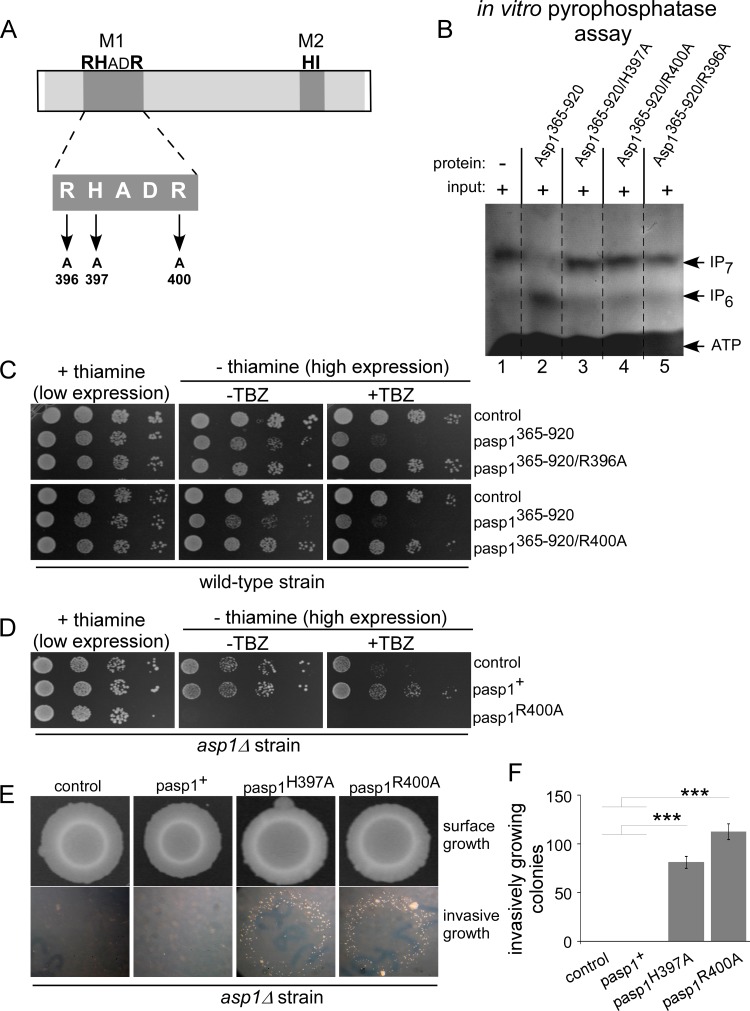
FIG 7.
The conserved amino acids of the M1 motif are essential for pyrophosphatase activity. (A) Diagrammatic representation of Asp1 pyrophosphatase M1 motif mutants. (B) In vitro pyrophosphatase assay using Asp1365–920, Asp1365–920/H397A, Asp1365–920/R400A, or Asp1365–920/R396A. Eight micrograms of the indicated proteins was added to Asp1 kinase-generated IP7 (input is shown in lane 1) and incubated for 16 h, and the resulting inositol polyphosphates were resolved on a 35.5% PAGE gel and stained with toluidine blue (−, without added component; +, with added component). All pyrophosphatase variants were tested at least twice in the in vitro assay. (C) Serial dilution patch tests (104 to 101 cells) of a wild-type strain transformed with vector (control) or plasmids expressing the indicated asp1 variants via the nmt1+ promoter. Transformants were grown under plasmid-selective conditions with or without thiamine and with or without 7 μg/ml TBZ at 25°C for 7 days. (D) Serial dilution patch tests (104 to 101 cells) of an asp1Δ strain transformed with vector (control) or plasmids expressing asp1+ or asp1R400A from the nmt1+ promoter. Transformants were grown as described for panel C. (E) Invasive-growth assay. A total of 105 asp1Δ cells transformed with a vector control or plasmid expressing asp1+, asp1H397A, or asp1R400A were grown on plasmid-selective thiamine-supplemented medium for 21 days at 30°C (surface growth). Removal of surface growth by washing revealed invasively growing colonies (bottom panels). (F) Quantification of invasively growing colonies. Per plasmid, three transformants were analyzed in triplicate. ***, P < 0.0005, t test. Numbers of invasive colonies: 81 ± 6 for the asp1H397A strain and 113 ± 8 for the asp1R400A strain.