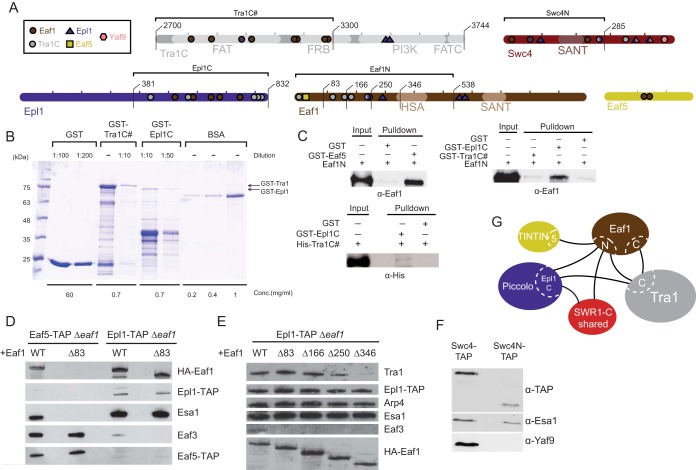
FIG 5.
Intersubunit connectivity analysis of NuA4 and its core scaffolding platform. (A) Subunits tested to analyze binding between NuA4 subunits. The locations of cross-linked residues and different construct lengths are indicated. (B) Example of how the amount of recombinant proteins used in GST pulldown assays was estimated. Portions (5 μl) of the indicated dilutions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue stain. A known BSA concentration was used to estimate the concentration of each fusion protein (full-length band) using ImageJ software. (C) Pulldown assays confirming direct interactions between NuA4 subunits. In vitro GST pulldown assays using the indicated recombinant proteins were performed, and the results were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Eaf1 or anti-His antibodies. The upper left panel shows that Eaf5 binds directly to the Eaf1 N-terminal region in vitro. rEaf1 (aa 1 to 538) is pulled down by GST-Eaf5. The upper right panel shows that the Eaf1 N-terminal region binds directly to the Epl1 C terminus in vitro. rEaf1N is pulled down by GST-Epl1 (region 381-832) but not by GST-Tra1 (region 2700-3300). In the lower left panel, His-Tra1 (region 2700-3300) shows a very weak interaction with GST-Epl1 (region 381-832) in vitro. The immunoblots shown here and in other panels of this figure are representative images from at least two independent experiments. (D) Eaf1 N-terminal 83 amino acids are required for association of the TINTIN module (Eaf5-Eaf7-Eaf3) to the NuA4 complex in vivo. NuA4 complexes were TAP purified using tagged Epl1 or Eaf5 from yeast strains expressing wild-type or N-terminally truncated Eaf1 and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA, anti-TAP, anti-Esa1, and anti-Eaf3 antibodies. (E) The Eaf1 N-terminal deletions identify a region required for the association of Tra1 to the NuA4 complex in vivo, in agreement with the cross-link data. NuA4 complexes were TAP purified using tagged Epl1 as in panel D from yeast strains expressing wild-type or different N-terminally truncated forms of Eaf1 and analyzed by Western blotting. (F) The C terminus of Swc4 is required for the association of Yaf9 to the NuA4 complex in vivo. NuA4 complexes were TAP purified from yeast strains expressing TAP-tagged wild-type Swc4 or its C-terminal truncated form (region 1-285) and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-TAP, anti-Esa1, and anti-Yaf9 antibodies. (G) Schematic of the major interaction regions identified by CXMS and biochemical analysis.