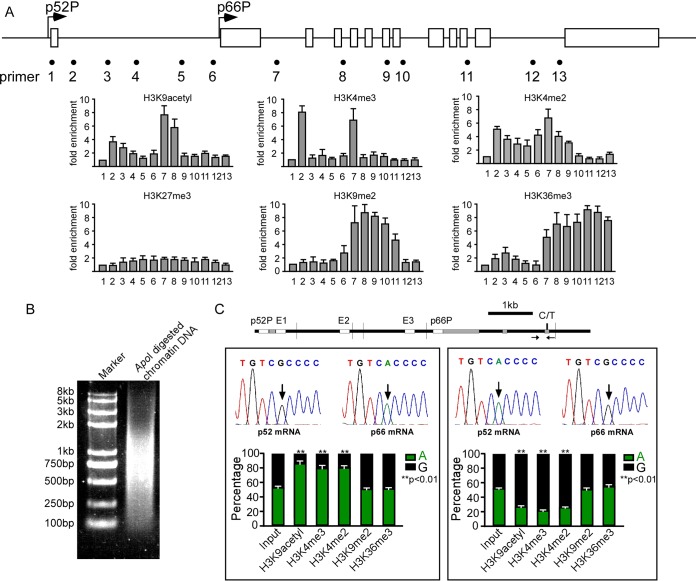
FIG 2.
Histone modifications mark differential alleles. (A) ChIP assay in HUVECs shows distributions of modified histones (K9 acetylated H3, K4 di- and trimethylated H3, K27 trimethylated H3, K9 dimethylated H3, and K36 trimethylated H3) along SHC1. Error bars indicate means ± standard deviations (SD) of three different ChIP experiments. (B) ApoI digestion efficiency in allele-specific ChIP assay. (C) Quantitative, nanofluidic, and allele-specific digital PCR was used to evaluate the percentages of genotypes of ChIP products in HUVECs generating p52Shc from the G allele and p66Shc from the A allele (left) and HUVECs generating p52Shc from the A allele and p66Shc from the G allele (right). Error bars indicate means ± SD for three different ChIP experiments.