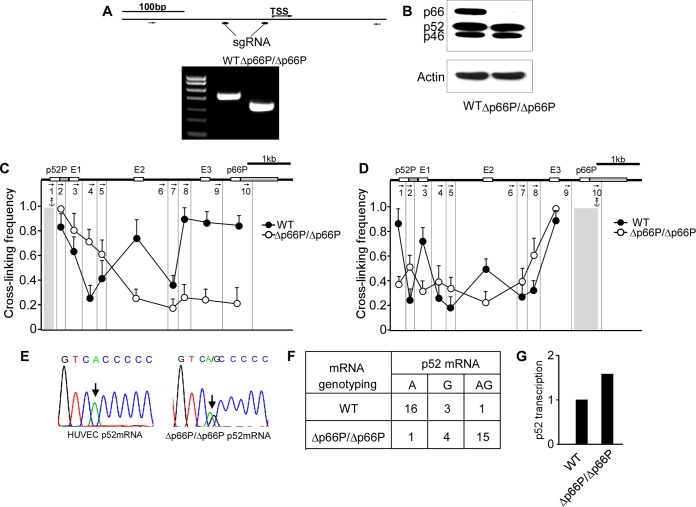
FIG 5.
Deletion of the p66Shc promoter results in a monoallelic-to-biallelic transcriptional switch of p52Shc. (A, top) Positions of sgRNAs used in CRISPR/Cas9 and PCR primers used for the PCR assay; (bottom) PCR products generated with the indicated primers. WT, normal HUVECs; Δp66P/Δp66P, HUVECs harboring homozygous p66Shc promoter deletions. (B) Immunoblots of Shc1 and actin in normal HUVECs and p66Shc promoter-deleted HUVECs. (C and D) 3C was performed to assess the change of chromatin configuration of SHC1 when the p66Shc promoter was deleted, with the DNA fragment harboring the p52Shc promoter (C) or the p66Shc promoter (D) as anchor. Error bars indicate means ± SD for three 3C experiments. (E) Representative traces of Sanger sequencing of RT-PCR products of p52Shc containing the informative exonic SNP (arrow) in normal HUVECs and p66Shc promoter-deleted HUVECs. (F) Quantitative analysis of Sanger sequencing of RT-PCR products of p52Shc containing the informative exonic SNP revealing alleles transcribing p52Shc in single HUVECs with the p66Shc promoter deletion. (G) Transcription of p52Shc in HUVECs and HUVECs with p66Shc promoter deletion, evaluated by quantitative and nanofluidic digital PCR assay.