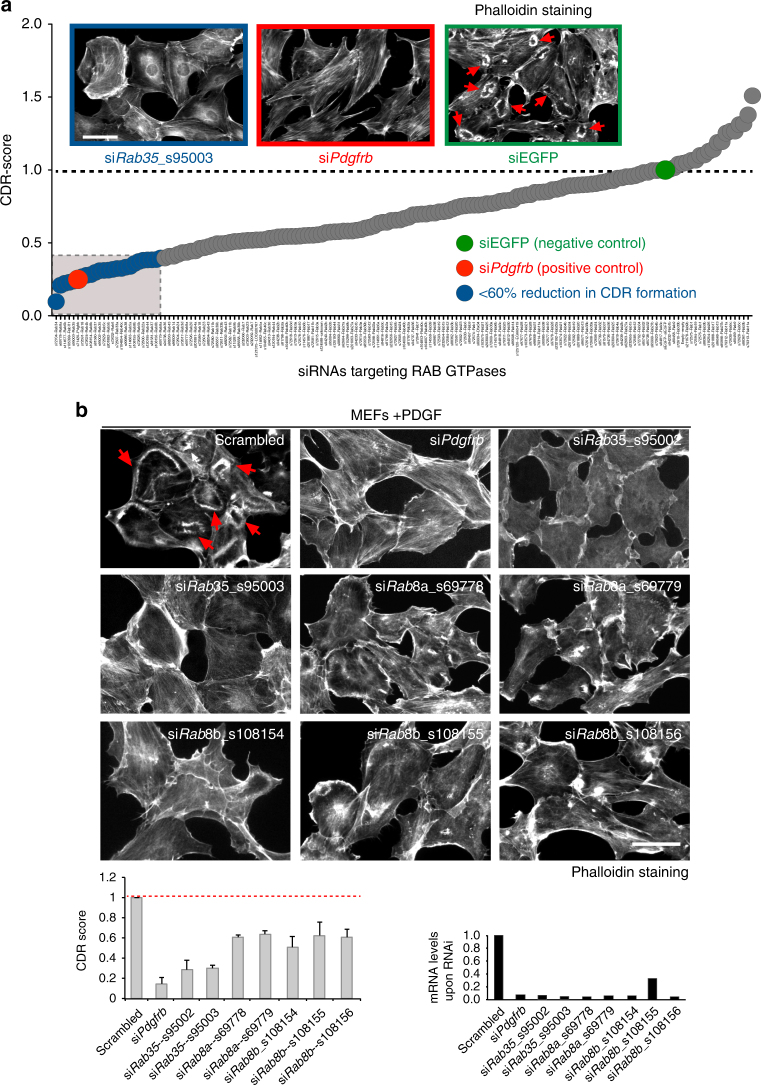
Fig. 1.
siRNA screening for RAB GTPases involved in CDRs formation. a siRNAs targeting RAB GTPases were ranked according to their CDR score (Methods and Supplementary Figure 1). Representative images of positive (siPdgfrb) and negative (siEGFP) controls are, respectively, in red and green. siRNAs best inhibiting CDR formation (more than 60% reduction relative to scrambled siEGFP) are enclosed into the light grey box. The oligo s95003 targeting Rab35, indicated in blue, is reported as a representative example. Red arrows indicate CDRs. Scale bar, 50 μm. b The siRNAs that inhibited CDRs formation more efficiently were validated in a completely independent experiment. Left: MEF cells interfered for Rab35 (ID: s95002, s95003), or Rab8a (ID: s69778, s69779), or Rab8b (ID: s108154, s108155, s108156), Pdgfrb (positive control), or Scrambled oligo (negative control). Upon PDGF stimulation, cells were fixed and stained with phalloidin. Representative images are shown for each experimental condition. Red arrows indicate CDRs. Scale bar, 50 µm. Right: CDRs were manually counted and normalized against scrambled-transfected, control samples. Data are the mean ± SD (n > 200 cells/condition in three independent experiments). The silencing of the targeted genes was verified by qRTPCR