Fig. 9.
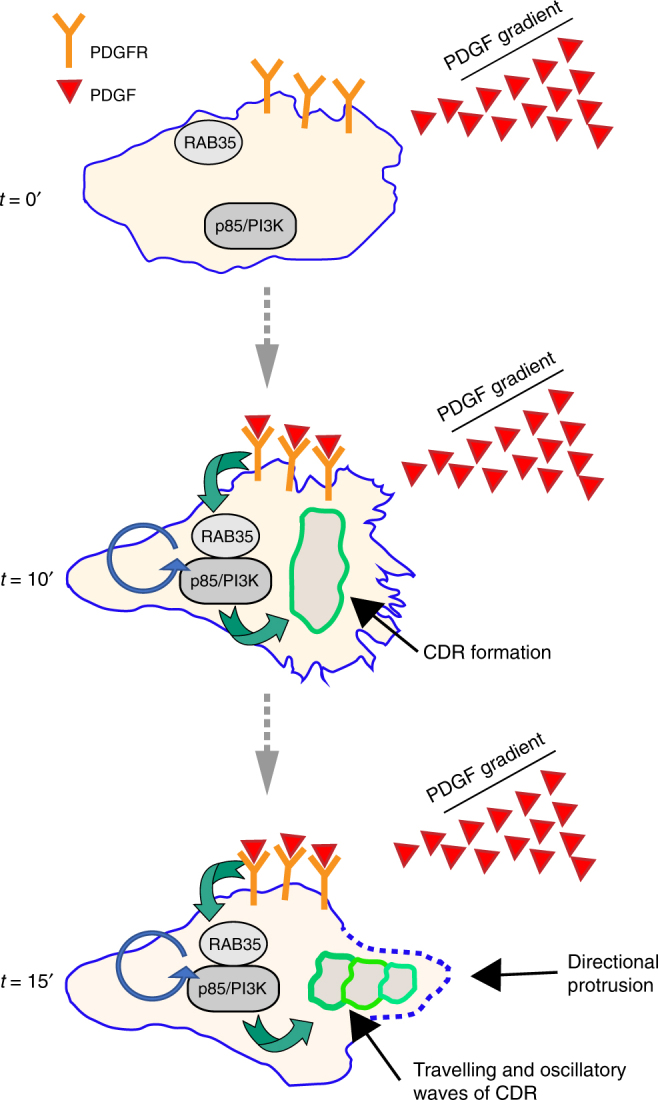
Model depicting the role of RAB35/p85–PI3K in CDR formation. Model depicting the role exerted by the RAB35–p85/PI3K axis in promoting the formation of excitable CDRs required to steer cells in response to PDGF (or HGF) stimulation. Top panel depict a mouse embryo fibroblast not exposed to PDGF gradients. RAB35 and p85/PI3K are not interacting. Middle panels, after few minutes upon exposure to PDGF (or HGF not depicted) gradients, PDGFR activation ensue, leading to the rapid formation of a RAB35–p85/PI3K complex. This cause the activation of PI3K that act upstream of RAC1 (not depicted) leading to the formation of apically localized CDRs. Lower panels, CDRs kinematics display a behaviour of oscillating and recurrent wave that travels along or expand centrifugally. Their formation is temporally correlated with the extension of directed cell protrusions. Thus, CDR display all the feature of an excitable oscillatory system that can be biased following chemotactic cues and contribute to stir cells along a chemotactic gradient
