Figure 5.
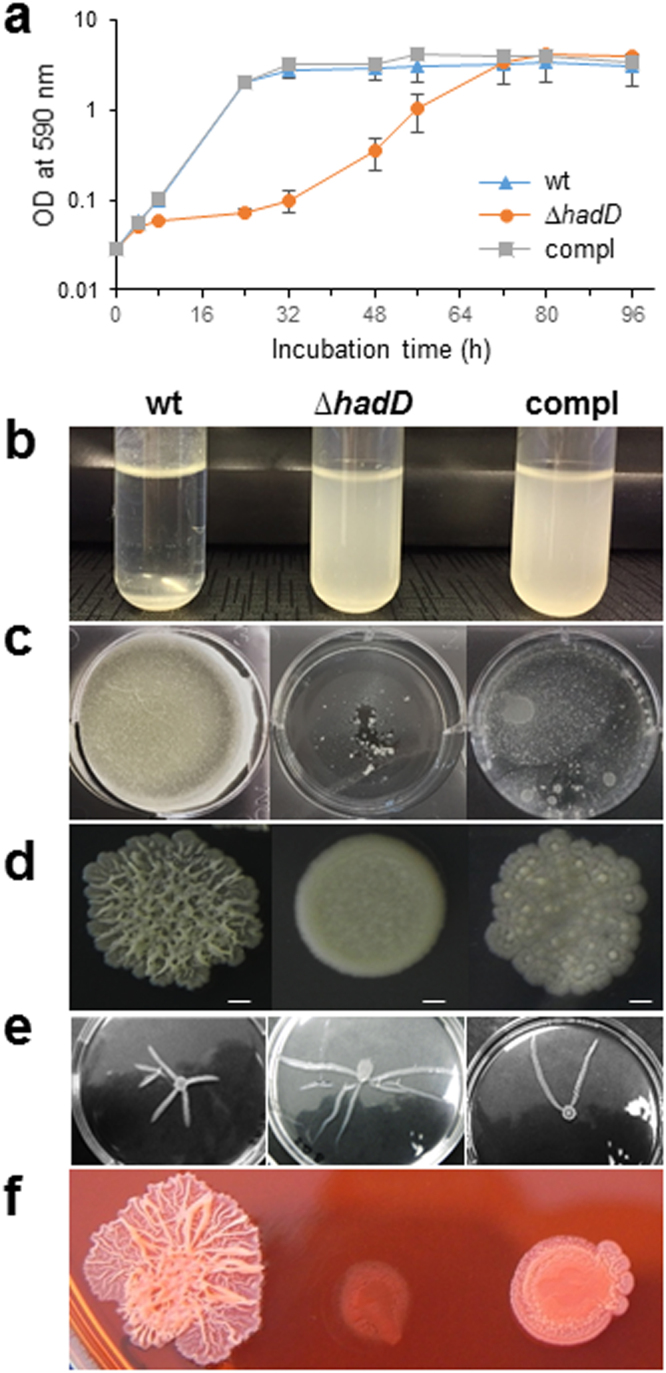
HadD deletion has an impact on bacterial fitness, assembly, spreading and surface hydrophobicity. Comparison of M. smegmatis wt, ∆hadD and complemented (compl) strains in different phenotyping assays. All the pictures are representative of three independent experiments. (a) Planktonic growth. Curves were established at 37 °C in 7H9-based medium supplemented with 0.05% (w/v) Tween-80. The cfu numbers determined at 0, 24 and 48 h confirmed a significant growth reduction for M. smegmatis ΔhadD. Data are means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. (b) Aggregation assays. Samples of cultures grown until saturation in 7H9-based medium without Tween were kept unshaken. Photographs correspond to the 15 min time point of the assays (Supplementary Fig. S9a). (c) Biofilm formation at the air-liquid interface. It was monitored on Sauton’s medium after 6 days of incubation at 37 °C. (d) Colony morphology. Five µl culture aliquots were spotted on 7H10-based medium. Scale bars represent 1 mm. (e) Sliding motility. It was monitored after 7 day incubation on semi-solid 7H9-based medium. Finger-like extensions appeared and spread outwards from the central inoculation point. M. smegmatis ∆hadD displayed a higher number and much longer extensions than the wt strain, whereas the complemented strain exhibited an intermediate extension number. For sliding motility quantification, see Supplementary Fig. S9b. (f) Colony morphology on Congo red. Five µl preculture aliquots were spotted on 7H10-based medium supplemented with 100 µg/ml Congo red. For quantification of Congo red binding, see Supplementary Fig. S9c.
