Fig. 5.
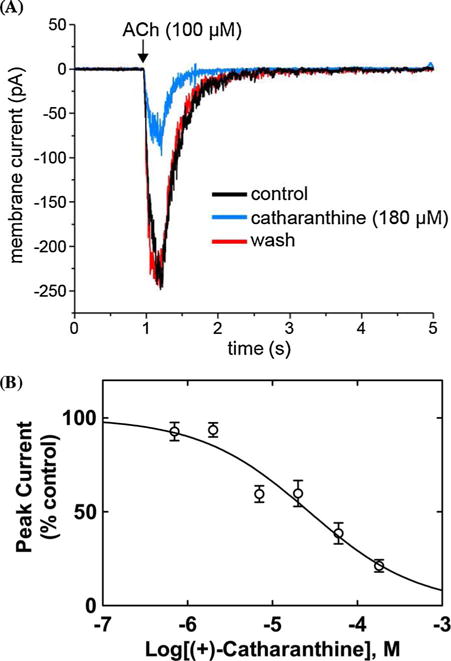
Inhibitory potency of (+)-catharanthine on ACh-evoked currents from MHb (VI) neurons. (A) ACh puffer (100 μM)-evoked currents from MHb (VI) neurons are decreased by 180 μM (+)-catharanthine. The puffer was performed for 250 ms at a pressure of 12 psi. After washing (10 min), the peak amplitude reached the same levels as that observed in control neurons, indicating a reversible inhibition. (B) Concentration-response relationship for the inhibitory activity of (+)-catharanthine on MHb (VI) neurons. Response was normalized to the maximal ACh response which was set as 100%. The plot (r2 = 0.87) is representative of 4–7 determinations, where the error bars are the S.D. The calculated IC50 and nH values are summarized in Table 2.
