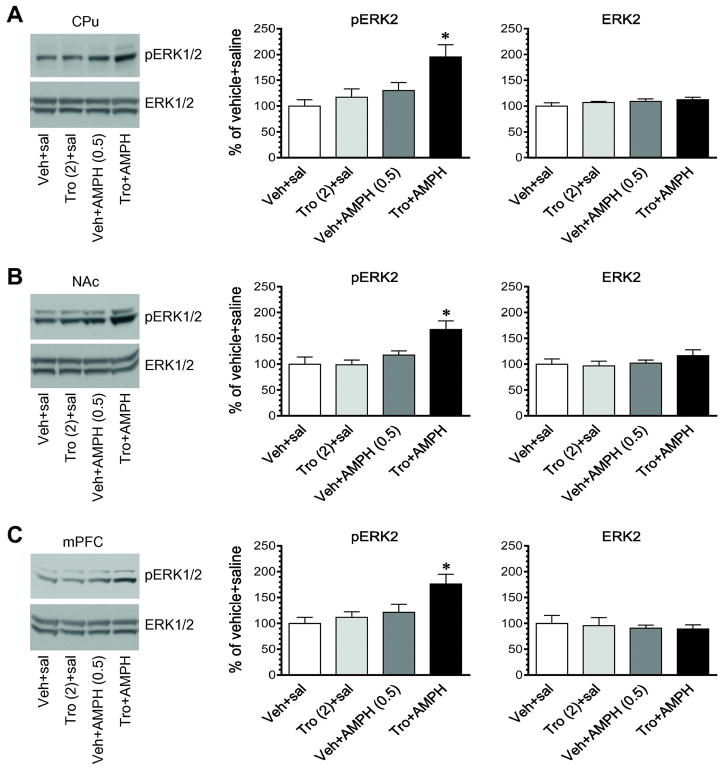
Figure 6. Effects of coadministration of tropicamide and AMPH at the subthreshold doses on phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2 in the striatum and mPFC.
A, Effects of coadministered tropicamide and AMPH on phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2 in the CPu. B, Effects of coadministered tropicamide and AMPH on phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2 in the NAc. C, Effects of coadministered tropicamide and AMPH on phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2 in the mPFC. Representative immunoblots are shown to the left of the quantified data. Note that coadministration of tropicamide and AMPH at subthreshold doses induced a significant increase in pERK2 signals in the CPu (A), NAc (B), and mPFC (C). Rats were given an i.p. injection of vehicle (Veh) or tropicamide (Tro, 2 mg/kg) 5 min prior to saline or AMPH (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) and were sacrificed 15 min after final injection for Western blot analysis of changes in pERK1/2 and ERK1/2 expression. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 4 per group) and were analyzed with two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc tests: pERK2 in the CPu (tropicamide: F(1,12) = 5.628, P = 0.035; AMPH: F(1,12) = 9.835, P = 0.0086; interaction: F(1,12) = 1.93, P = 0.19), NAc (tropicamide: F(1,12) = 4.577, P = 0.054; AMPH: F(1,12) = 13.34, P = 0.003; interaction: F(1,12) = 5.003, P = 0.045), and mPFC (tropicamide: F(1,12) = 5.216, P = 0.041; AMPH: F(1,12) = 8.697, P = 0.012; interaction: F(1,12) = 2.32, P = 0.154). *p < 0.05 versus vehicle + saline.